|
|
| (11 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{Huge|Flavonoid}} | + | {{Huge|{{Bilingual|フラボノイドのデータベース|Flavonoid Database}}}} |
| − | [[Image:FL.gif|thumb|150px|right|Figure 1: The Backbone of Flavonoid Structure]]
| + | {| |
| − | | + | | __TOC__ |
| | + | |} |
| | {{Flavonoid/Header}} | | {{Flavonoid/Header}} |
| | | | |
| Line 8: |
Line 9: |
| | {{Twocolumn | | {{Twocolumn |
| | | | | | |
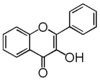
| − | The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin ''flavus'' (yellow) with ''oid'', meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See [[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]). | + | The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin ''flavus'' (yellow), meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See [[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]). |
| − | <br/>
| + | |
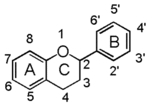
| − | Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).
| + | |
| − | The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
| + | |
| − | <br/>
| + | |
| − | Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone.
| + | |
| | | | | | |
| | フラボノイドの語源は,ラテン語の flavus (黄色)に「~のような」という意味の oid をつけたものです。これは代表的なフラボンであるquercetinやkaempferolが広く使われてきた黄色の天然色素であることに由来しています ([[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]参照)。 | | フラボノイドの語源は,ラテン語の flavus (黄色)に「~のような」という意味の oid をつけたものです。これは代表的なフラボンであるquercetinやkaempferolが広く使われてきた黄色の天然色素であることに由来しています ([[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]参照)。 |
| − | <br/>
| + | }} |
| | + | {{Twocolumn |
| | + | | |
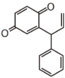
| | + | In chemistry terms, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). |
| | + | The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1). |
| | + | | |
| | 化学的な定義でフラボノイドとは, ベンゼン環2個 (それぞれA環B環と呼ばれる) を3つの炭素 (C) で結合した, 植物の代謝産物の総称です (Figure 1)。 | | 化学的な定義でフラボノイドとは, ベンゼン環2個 (それぞれA環B環と呼ばれる) を3つの炭素 (C) で結合した, 植物の代謝産物の総称です (Figure 1)。 |
| − | Figure 1 において 2,3,4 と番号付けされた炭素鎖は A 環の水酸基と結合して C 環を構成します。フラボノイドのカテゴリーは,たいてい C 環の修飾パターンで決まります (Table 1)。 | + | Figure 1 において 2,3,4 と番号付けされた炭素鎖は A 環の水酸基と結合して C 環を構成します。フラボノイドのカテゴリーは,たいてい C 環の修飾パターンで決まります (Table 1)。}} |
| − | <br/>
| + | [[Image:FL.gif|thumb|150px|right|Figure 1: The Backbone of Flavonoid Structure]] |
| | + | {{Twocolumn |
| | + | | |
| | + | Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Well known names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone. |
| | + | | |
| | フラボノイドの用途は 色素から食品添加物まで多様です。 よく耳にするものでは, アントシアニン, カテキン, フラバン(茶), イソフラボンなど, 全てフラボノイドです。 | | フラボノイドの用途は 色素から食品添加物まで多様です。 よく耳にするものでは, アントシアニン, カテキン, フラバン(茶), イソフラボンなど, 全てフラボノイドです。 |
| | }} | | }} |
| Line 29: |
Line 34: |
| | !colspan="3"|1st Class | | !colspan="3"|1st Class |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
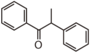
| − | |[[:Category:FL1|FL1: Anthochlor<br/> (Aurone and Chalcone)]]<br>オーロン、カルコン<br>[[Image:Fl1.png|100px]]<br>safflower yellow<br>紅花(末摘花)の黄色 | + | |[[:Category:FL1|FL1: Anthochlor<br/>({{Bilingual|オーロン、カルコン|Aurone and Chalcone}})]]<br/> |
| − | |[[:Category:FL2|FL2: Flavanone]]<br>フラバノン<br>[[Image:Fl2.png|100px]]<br>white skin of orange<br>みかんジュースの白沈 | + | [[Image:Fl1.png|100px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|紅花(末摘花)の黄色|safflower yellow}} |
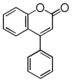
| − | |[[:Category:FL3|FL3: Flavone]]<br>フラボン<br>[[Image:Fl3.png|100px]]<br>herbs like parsley<br>セロリやパセリ等ハーブ | + | |[[:Category:FL2|FL2: {{Bilingual|フラバノン|Flavanone}}]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fl2.png|100px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|みかんジュースの白沈|white skin of orange}} |
| | + | |[[:Category:FL3|FL3: {{Bilingual|フラボン|Flavone}}]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fl3.png|100px]]<br>{{Bilingual|セロリやパセリ等ハーブ|herbs like parsley, yellow dye}} |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
| | | | | | |
| Line 46: |
Line 54: |
| | |[[:Category:FL1D|FL1D]]||[[:Category:FL1D|Dihydrochalcone]]<br>[[Image:Fl1d.png|120px]] | | |[[:Category:FL1D|FL1D]]||[[:Category:FL1D|Dihydrochalcone]]<br>[[Image:Fl1d.png|120px]] |
| | |} | | |} |
| − | | [[:Category:FL2F|FL2F: Flavanone]] | + | | |
| − | | [[:Category:FL3F|FL3F: Flavone]] | + | | |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
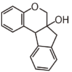
| − | |[[:Category:FL4|FL4: Dihydroflavonol]]<br/>ジヒドロフラボノール<br>[[Image:Fl4.png|100px]]<br/>antioxidant in grapes<br/>ブドウの抗酸化成分 | + | |[[:Category:FL4|FL4: {{Bilingual|ジヒドロフラボノール|Dihydroflavonol}}]]<br/> |
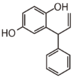
| − | |[[:Category:FL5|FL5: Flavonol]]<br>フラボノール<br>[[Image:Fl5.png|100px]]<br/>vegetables such as onion<br>たまねぎ等多くの野菜 | + | [[Image:Fl4.png|100px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|ブドウの抗酸化成分|antioxidant in grapes}} |
| − | |[[:Category:FL6|FL6: Flavan]]<br/>Leucoanthocyanidin<br/>フラバン<br>[[Image:Fl6.png|100px]]<br/>tea, cocoa<br/>お茶、ココア | + | |[[:Category:FL5|FL5: {{Bilingual|フラボノール|Flavonol}}]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fl5.png|100px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|たまねぎ等多くの野菜|vegetables such as onion}} |
| | + | |[[:Category:FL6|FL6: {{Bilingual|フラバン|Flavan}}<br/>({{Bilingual|ロイコアントシアニジン|Leucoanthocyanidin}})]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fl6.png|100px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|お茶、ココア|tea, cocoa}} |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
| − | | [[:Category:FL4D|FL4D: Dihydroflavonol]] | + | | |
| − | | [[:Category:FL5F|FL5F: Flavonol]] | + | | |
| | | | | | |
| | {| class="collapsible collapsed" border="1" cellspacing="0" width="150" | | {| class="collapsible collapsed" border="1" cellspacing="0" width="150" |
| Line 69: |
Line 80: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
| − | |[[:Category:FL7|FL7: Anthocyani(di)n]]<br>アントシアニ(ジ)ン<br>[[Image:Fl7.png|120px]]<br>purple vegetables/fruits<br>(赤)紫の野菜、果物 | + | |[[:Category:FL7|FL7: {{Bilingual|アントシアニ(ジ)ン|Anthocyani(di)n}}]]<br/> |
| − | |[[:Category:FLI|FLI: Isoflavonoid]]<br>イソフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fli.png|100px]]<br>beans<br>豆類 | + | [[Image:Fl7.png|120px]]<br/>{{Bilingual|(赤)紫の野菜、果物|purple vegetables/fruits}} |
| − | |[[:Category:FLN|FLN: Neoflavonoid]]<br>ネオフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fln.png|75px]] | + | |[[:Category:FLI|FLI: {{Bilingual|イソフラボノイド|Isoflavonoid}}]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fli.png|100px]]<br>{{Bilingual|豆類|beans}} |
| | + | |[[:Category:FLN|FLN: {{Bilingual|ネオフラボノイド|Neoflavonoid}}]]<br/> |
| | + | [[Image:Fln.png|75px]] |
| | |- valign="top" | | |- valign="top" |
| | | | | | |
| Line 126: |
Line 140: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | </center> | | </center> |
| − | <!--- Class Information (Do not delete. It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) | + | <!--- Class Information (Do not delete. This list is used by Template:Hierarchy.) |
| | &&FL&&Flavonoid&& | | &&FL&&Flavonoid&& |
| | &&FL1&&Aurone and Chalcone&& | | &&FL1&&Aurone and Chalcone&& |
| Line 165: |
Line 179: |
| | ---> | | ---> |
| | | | |
| − | =={{Bilingual|生合成|Biosynthesis}}== | + | ==[[:Category:FL/Biosynthesis|{{Bilingual|生合成のページヘ|Biosynthesis}}]]== |
| | | | |
| − | {{Twocolumn | + | ==[[:Category:FL/Bioactivity|{{Bilingual|生物活性のページヘ|Bioactivity}}]]== |
| − | |Flavonoid is synthesized through both the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway and the acetate-malonate pathway in all higher plants (but not algae). Most plants contain the 7 major subgroups (chalcones, flavanones, flavones, flavonols, flavans, anthocyanidins, and anthycyanins), but aurones or isoflavonoids are not ubiquitous. | + | |
| − | |フラボノイドは全ての高等植物においてフェニルプロパノイド経路および酢酸-マロン酸経路の両方を用いて生成され (海草では異なる)、ほとんどの植物は7つの大きなグループ (カルコン、フラバノン、フラボン、フラボノール、フラバン、アントシアニジン、アントシアニン) を含みます。しかしオーロンやイソフラボノイドは全ての植物に含まれるわけではありません。 | + | |
| − | }} | + | |
| | | | |
| − | <!----一般にポリフェノール類は
| |
| − | # フェニルプロパノイド経路 から生合成されるもの と
| |
| − | # 酢酸-マロン酸経路 から生合成されるもの
| |
| − | にわかれます。 たとえば, 1 では、クマリン, リグナン, リグニンなどが生合成され, 2 の酢酸-マロン酸経路では, アントラキノンが知られています。
| |
| − | フラボノイドは, 上記 2 つの, 脂肪酸フェニルプロパノイド経路と 酢酸-マロン酸パスウェイとの 組み合わせにより生合成されます。 同様のパスウェイから生成される産物には, キサントン, スチルベンなどがあります。
| |
| − | ----->
| |
| | | | |
| − | {| style="text-align:center"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="4"| 4-coumaroyl CoA + malonyl CoA
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]CHS
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:gold"| [[Image:fl1.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL1|''CHALCONES, AURONES'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:gold"| [[FL1CAANS0001|chalconaringenin]]<br/>[[Image:FL1CAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:palegoldenrod"| [[Image:fl3.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL2|''FLAVONES'']]
| |
| − | | colspan="2" style="background:palegoldenrod" | [[FL3FAANS0001|apigenin]]<br/>[[Image:FL3FAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | colspan="2" style="background:palegoldenrod" | [[FL3FACNS0001|luteolin]]<br/>[[Image:FL3FACNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | CHI [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] <small>(isomerase)</small>
| |
| − | | colspan="3" style="text-align:left" | [[Image:Arrow00ur35.png]]FS <small>(oxygenase)</small>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align:right"|<br/>IFS [[Image:Arrow00dl35.png]]
| |
| − | | style="background:pink"| [[FL2FAANS0001|naringenin]]<br/> [[Image:fl2.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL2|''FLAVANONE'']]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:yellowgreen"| [[FL5FAANS0001|kaempferol]]<br/>[[Image:FL5FAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="background:yellowgreen" colspan="3" | [[Image:fl5.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL5|''FLAVONOLS'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:yellowgreen"| [[FL5FACNS0001|quercetin]]<br/>[[Image:FL5FACNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:yellowgreen"| [[FL5FAGNS0001|myricetin]]<br/>[[Image:FL5FAGNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:navajowhite"| [[Image:fli.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FLI|''ISO-FLAVONES'']]
| |
| − | | F3H [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] <small>(hydroxylase)</small>
| |
| − | | colspan="4" style="text-align:left"|[[Image:Arrow00ur35.png]] FLS <small>(oxygenase)</small>
| |
| − | | colspan="2" style="text-align:left"|[[Image:Arrow00ur35.png]] FLS
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | colspan="2" style="text-align:left"|[[Image:Arrow00ur35.png]] FLS
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:plum"| [[Image:fl4.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL4|''DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:plum"| [[FL4DAANS0001|dihydro-kaempferol]]<br/>[[Image:FL4DAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | colspan="3"| F3'H<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r100.png]]<br/>+OH in B-ring
| |
| − | | style="background:plum"| [[FL4DACNS0001|dihydro-quercetin]]<br/>[[Image:FL4DACNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | colspan="3"| F3'5'H<br/>[[Image:Arrow00r100.png]]<br/>+OH in B-ring
| |
| − | | style="background:plum"| [[FL4DAGNS0001|dihydro-myricetin]]<br/>[[Image:FL4DAGNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | DFR [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] <small>(reductase)</small>
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]DFR
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]DFR
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:skyblue"| [[Image:fl6d.png|50px]]<small>flavan diol</small><br/> [[:Category:FL6|''LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:skyblue"| [[FL6DAANS0001|leuco-pelargonidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL6DAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="text-align:left;vertical-align:bottom" colspan="3"|
| |
| − | {|
| |
| − | |[[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | {|
| |
| − | |<small>(reductase)</small>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | LAR
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | style="background:skyblue"| [[FL6DACNS0001|leuco-cyanidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL6DACNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="text-align:left;vertical-align:bottom" colspan="3"|[[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]] LAR
| |
| − | | style="background:skyblue"| [[FL6DAGNS0001|leuco-delphinidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL6DAGNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="text-align:left;vertical-align:bottom" colspan="2"|[[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]] LAR
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | LDOX [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] <small>(oxygenase)</small>
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:olive"| ''PROANTHO- CYANIDINS'' *
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] LDOX
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:olive"| ''PROANTHO- CYANIDINS'' *
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] LDOX
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:olive"| *...polymers of flavanols
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:tomato"| [[Image:fl7_2.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL7|''ANTHO-CYANIDINS'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:tomato"| [[FL7AAANS0001|pelargonidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AAANS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="vertical-align:bottom" colspan="2" | [[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]]ANR [[Image:Arrow00u.png]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:tomato"| [[FL7AACNS0001|cyanidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AACNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="vertical-align:bottom" colspan="2" | [[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]]ANR [[Image:Arrow00u.png]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:tomato"| [[FL7AAGNS0001|delphinidin]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AAGNS0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="vertical-align:bottom" colspan="2" | [[Image:Arrow00dr35.png]]ANR [[Image:Arrow00u.png]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | UF3GT [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]] <small>(+sugar)</small>
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:tan"| [[FL63AANS0002|epi-afzelechin]]<br/>[[Image:FL63AANS0002.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]UF3GT
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:tan"| [[FL63ACNS0002|epi-catechin]]<br/>[[Image:FL63ACNS0002.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]UF3GT
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:tan"| [[FL63AGNS0003|epigallo-catechin]]<br/>[[Image:FL63AGNS0003.png|70px]]
| |
| − | | style="background:tan"| [[Image:fl6.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL6|''FLAVAN 3-OLS'']]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="background:mediumpurple"| [[Image:fl7.png|50px]]<br/>[[:Category:FL7|''ANTHO-CYANINS'']]
| |
| − | | style="background:mediumpurple"| [[FL7AAAGL0002|pelargonidin 3-glucoside]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AAAGL0002.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:mediumpurple"| [[FL7AACGL0001|cyanidin 3-glucoside]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AACGL0001.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | style="background:mediumpurple"| [[FL7AAGGL0002|delphinidin 3-glucoside]]<br/>[[Image:FL7AAGGL0002.png|70px]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | {|
| |
| − | |[[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]
| |
| − | |UF5GT, AOMT etc.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | {|
| |
| − | |[[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]
| |
| − | |UF5GT, AOMT etc.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | {|
| |
| − | |[[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]
| |
| − | |UF5GT, AOMT etc.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed"
| |
| − | ! colspan=4| {{Bilingual|上記遺伝子略称の詳細 (英語)|Information for the Above Abbreviated Gene Names}}
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! colspan=4| Six Structural Genes
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! Abbrev. || Name || Origin || Information
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | CHS
| |
| − | | chalcone synthase
| |
| − | | Bacterial polyketide synthases, particularly those in fatty acid synthesis (Verwoert et al. 1992)
| |
| − | | Early response against light <ref>Kubasek WL, Shirley BW, McKillop A, Goodman HM, Briggs W, Ausubel FM: Regulation of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in germinating Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 1992 4:1229-1236</ref> <ref>Pelletier MK, Murrell JR, Shirley BW: Characterization of flavonol synthase and leucoanthocyanidins dioxygenase genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 1997 113:1437-1445</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | CHI
| |
| − | | chalcone-flavanone isomerase
| |
| − | | Unclear and unique to plants.<ref>Jez JM, Bowman ME, Dixon RA, Noel JP: Structure and mechanism of chalcone isomerase: an evolutionarily unique enzyme in plants. Nat Struct Biol 2000 7: 786?791</ref>
| |
| − | ''Eubacterium ramulus'' has the CHI activity. <ref>Herles C, Braune A, Braut M: First bacterial chalcone isomerase isolated from ''Eubacterium ramulus''. Arch Microbiol 2004 181:428-434.</ref>
| |
| − | | Early response against light.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | F3H
| |
| − | | flavanone 3-hydroxylase
| |
| − | | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family <ref>Winkel-Shirley B: Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology and biotechnology. Plant Physiol 2001 126:485-492</ref>
| |
| − | | Early response in Arabidopsis but late in Antirrhinum <ref>Martin C, Prescott A, Mackay S, Bartlett J, Vrijlandt E: Control of anthocyanin biosyntehsis in flowers ''Antirrhinum majus''. Plant J 1991 1:37-49</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | FLS
| |
| − | | flavonol synthase
| |
| − | | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family <ref>Holton TA, Cornish EC: Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1993 7:1071-1083</ref>
| |
| − | | Early response against light. In Arabidopsis, all structural genes are single-copy except for this one, to which six genes exist and two of them are not expressed.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DFR
| |
| − | | dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
| |
| − | | NADPH-dependent reductase associated with steroid metabolism <ref>Baker ME, Blasco RE: Expansion of the mammalian 3bhydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/plant dihydroflavonol reductase superfamily to include a bacterial cholesterol dehydrogenase, a bacterial UDP-galactose 4-epimerase, and open reading frames in vaccinia virus and fish lymphocystis disease virus.
| |
| − | FEBS Lett 1992 301: 89?93</ref>
| |
| − | | Later response
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | ANS/LDOX
| |
| − | | anthocyanidin synthase or leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase
| |
| − | | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family
| |
| − | | Later response
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! colspan=4| Auxiliary Genes
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | F3'H
| |
| − | | flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase
| |
| − | | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family <ref>Brugliera F, Barri-Rewell G, Holton TA, Mason JG: Isolation and characterization of a flavonoid 3-hydroxylase. cDNA clone corresponding to the Ht1 locus of Petunia hybrida. Plant J 1999 19: 441?451</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | F3'5'H
| |
| − | | flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase
| |
| − | | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family <ref>Holton TA, Brugliera F, Lester DR, Tanaka Y, Hyland CD, Menting JGT, Lu CY, Farcy E, Stevenson TW, Cornish EC: Cloning and expression of cytochrome P450 genes controlling flower colour. Nature 1993 366:276?279</ref>
| |
| − | | Not reported in mosses or liverworts. The transformation of the F3'5'H and the cytochrome b5 gene of petunia into carnation changed its flower color deep purple.<ref>de Vetten N, ter Horst J, van Schaik H-P, de Boer A, Mol J, Koes R: A cytochrome b5 is required for full activity of flavonoid 39,59-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 involved in the formation of blue flowers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999 96: 778?783</ref><ref>Brugliera F, Tull D, Holton TA, Karan M, Treloar N,
| |
| − | Simpson K, Skurczynska J, Mason JG: Introduction of a cytochrome b5 enhances the activity of flavonoid 3'5' hydroxylase (a cytochrome P450) in transgenic carnation. Sixth International Congress of Plant Molecular Biology. University of Laval, Quebec, 2000 pp S6?S8</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | FSI
| |
| − | | flavone synthase
| |
| − | | Dioxygenase in parsley (FSI) and P450 monooxygenase in snapdragon (FSII).
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | LAR (or LCR)
| |
| − | | leucoanthocyanidin reductase
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | UF3GT
| |
| − | | UDP flavonoid glucosyltransferase
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | GST
| |
| − | | glutathione-S-transferase
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | | Transport of flavonoids from cytoplasm to vacuole or cell walls requires both GST and the glutathione pump in ATP-binding cassette family.<ref>Marrs KA, Alfenito MR, Lloyd AM, Walbot V: A glutathione S-transferase involved in vacuolar transfer encoded by the maise gene Bronze-2. Nature 1995 375: 397?400</ref><ref>Alfenito MR, Souer E, Goodman CD, Buell R, Mol J, Koes R, Walbot V: Functional complementation of anthocyanin sequestration in the vacuole by widely divergent
| |
| − | glutathione S-transferases. Plant Cell 1998 10: 1135?1149</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | AOMT
| |
| − | | anthocyanin O-methyl transferase
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="4"| <references/>
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | =={{Bilingual|生物活性|Bioactivity}}==
| |
| − | ==={{Bilingual|お茶|Tea Related}}===
| |
| − | * [[Doc:Tea|Tea category]] 茶の種類
| |
| − | * [[Doc:Tea/Consumption|Tea consumption]] 茶の消費量
| |
| − | * [[Doc:Tea/Health|Tea and health]] 茶と健康
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==={{Bilingual|フラボノイド一般|General Flavonoid}}===
| |
| − | {{Twocolumn|
| |
| − | ;All flavonoids
| |
| − | ''photoprotectant, anti-oxidant'' <br/>
| |
| − | Not only anthocyanins but even simple structures such as chalcone can absorb UV wavelengths strongly. The ability of photoprotection is derived from its anti-oxidative activity. For example, quercetin is a more effective photoprotectant and anti-oxidant than kaempferol. <ref name="Ryan 2002">Ryan KG, Swinny EE, Markham KR, Winefield C (2002) "Flavonoid gene expression and UV photoprotection in transgenic and mutant Penunia leaves" Phytochem 59:23-32 PMID 11754940</ref>
| |
| − | <ref>Li J, Ou-Lee T-M, Raba R, Amundson RG, Last RL (1993) "Arabidopsis flavonoid mutants are hypersensitive to UV-B irradiation" Plant Cell 5: 171-179 PMID 12271060</ref>
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | ;全フラボノイド
| |
| − | ''抗紫外線、抗酸化作用'' <br/>
| |
| − | アントシアニンだけでなく、カルコンのような構造の簡単なフラボノイドでも紫外線をよく吸収します。効紫外線効果は効酸化作用に関係しています。例えばクエルセチンはケンフェロールよりも効紫外線と効酸化作用がともに強くなります。
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | <references/>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * [Doc:Antioxidant|{{Bilingual|抗酸化作用の詳細|Details of antioxidant activity}}]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Twocolumn
| |
| − | |'''Flavanols'''<br/>
| |
| − | Quercetin in onions and flavanols in cocoa are said to reduce blood pressure in hypertensive animals <ref>Hooper L, Kroon PA, Rimm EB, et al. (2008) "Flavonoids, flavonoid-rich foods, and cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials" Am J Clin Nutr 88:38–50 PMID 18614722</ref>, but their effect or mechanism is not clinically conclusive.
| |
| − | |'''フラバノール'''<br/>
| |
| − | 玉葱のクエルセチンやココアのフラバノールは血圧降下作用があるといわれますが、その効果や医学的メカニズムははっきりしていません。
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <references/>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{Twocolumn
| |
| − | |'''Tannins (proanthocyanidins)'''
| |
| − | ''anti-bacteria, anti-fungi''
| |
| − | |'''タンニン (プロアントシアニジニン)'''
| |
| − | ''抗菌、抗カビ作用''
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | =={{Bilingual|利用効率|Bioavailability}}==
| |
| − | {| class ="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! Flavonoid || Dose || Observation
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | catechin<ref>Das NP (1971) ''Biochem Pharmacol'' 20, 3435-3445</ref> || 5.8 g || 26% was excreted within 24h. ''m''-hydroxyphenyl propionic acid was detected in plasma after 6h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-O-methyl-catechin<ref>Hackett AM, Griffiths LA, Wermeille M (1985) ''Xenobiotica'' 15, 907-914</ref> || 2 g || plasma level 11-18 ug/ml within 2h; 38% was excreted as glucuronides and sulphates in urine within 120h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | quercetin<ref>Hollman PCH et al (1995) ''Am J Clin Nutr'' 62, 1276-1282; Hollman PCH et al (1996) ''Free Rad Biol Med'' 21, 703-707</ref> || 64 mg (as fried onion) || plasma level 1 uM, 2h later
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | quercetin<ref>Gugler R, Leshik M, Dengler HV (1975) ''Eur J Clin Pharmacol'' 9, 229-234</ref> || 4 g (as supplement) || undetected in urine or plasma
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | decaffeinated green tea<ref>Lee MT et al (1995) ''Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev'' 41,393-399</ref> || 88 mg EGCG, 82 mg EGC, 33 mg ECG, and 32 mg EC || plasma level 46-268 ng/ml, 82-206 ng/ml, undetected, and 40-80 ng/ml, respectively.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ; Isoflavones
| |
| − | Isoflavones are efficiently absorbed from the colon and exhibit the highest bioavailability. (Usually polyphenols absorbed from the colon show very low availability.) Daidzein and genistein are known to form chlorinated products (e.g. 3- and 8-chlorodaidzein), then are conjugated with glucuronides and excreted in bile.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ; Anthocyanins
| |
| − | Although anthocyanins comprise ca. 50% of total polyphenols, they are poorly available (less than 1% of intake in urinary levels). Anthocyanins are absorbed from the stomach, and their glycosides appear in plasma soon after the intake. In blood, only anthocyanins exist in a non-conjugated form.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ; Flavan
| |
| − | Flavan 3-ols and phenolic acids are efficiently abosrbed from the small instestine, a few hours after intake.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ; Others
| |
| − | Non-absorbed flavonoids are transported to the colon, and subjected to metabolism by microbiota. These flavonoids are therefore absorbed much less compared to flavan 3-ols and phenolic acids. Esterification of phenolic acids (e.g. chlorogenic acid), however, reduces absorption.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | During absorption, polyphenols are metabolized to form β-glucuronide and sulfate conjugates (phase II conjugation in the intestinal wall), and catechol units are methylated. C-glycosides such as puerarin remain stable and not conjugated. These metabolized forms show markedly different bioactivities from their aglycones.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <references/>
| |
| − | <!---
| |
| − | =={{Bilingual|代表例|Representative Names}}==
| |
| − | <div style="column-count:2; -moz-column-count:2;">
| |
| − | * [[:Category:FLI|isoflavonoid]] in beans (豆のイソフラボン)
| |
| − | * [[:Category:FL7|anthocyanin]] in berries (ベリーのアントシアニン)
| |
| − | * [[FL63ACNS0001|catechin]] in tea (お茶のカテキン)
| |
| − | * [[FL5FACGL0013|rutin]] in buckwheat (ソバのルチン)
| |
| − | * [[FL2FAEGS0001|hesperidin]] in orange (ミカンのヘスペリジン)
| |
| − | * [[FL1CAANS0001|naringenin chalcone]] in tomato (トマトのナリンゲニンカルコン)
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | --->
| |
| | =={{Bilingual|データベース統計|Database statistics/ranking}}== | | =={{Bilingual|データベース統計|Database statistics/ranking}}== |
| | {{#DEF:NumberOfMolecules|{{#countTitle:FL|}}}} | | {{#DEF:NumberOfMolecules|{{#countTitle:FL|}}}} |
In chemistry terms, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).
The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Well known names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone.
This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references. Currently, 6961 flavonoid structures, 3961 plant species, and 5215 references describing total 19861 metabolite-species relationships are registered.
Flavanones are rich in citrus, not in vegetables.
Many herbs contain flavones. Parsley is rich in apigenin; celery and thyme in luteolin.
Flavonols are prevalent in vegetables, usually in small amounts. Onions, kales, hot peppers are good sources.
Catechins and epicatechins are contained in legumes and teas, but not in other vegetables.
Anthocyanins are contained in berries. Vegetables supply only small amounts.
The following vegetables and herbs have flavonoid contents less than 5 mg/100 g:
beets, kidney beans, snap beans, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, cucumber, endive, gourd, leek, lettuce, green peas, sweet pepper, potato, radish, tomato, oregano, perrilla, rosemary
Currently unused.
The flavonoid IDs used in this site is the same as those in Flavonoid Viewer in metabolome.jp except for the following FL7 category.