Category:FL
Contents |
FL: Flavonoid フラボノイド
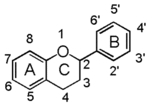
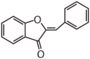
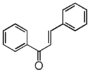
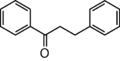
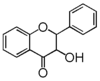
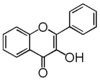
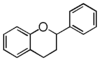
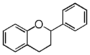
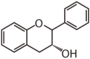
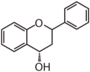
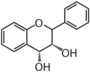
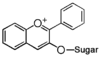
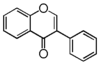
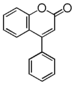
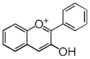
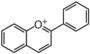
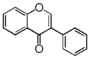
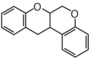
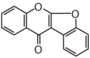
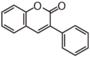
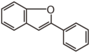
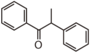
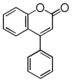
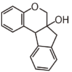
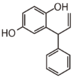
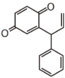
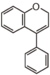
<p> The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin flavus (yellow) with oid, meaning yellow-ish. It is probably due to its function as (yellow) flower pigments. Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan (tea), and isoflavone.
</p>
Biosynthesis 生合成
<p> Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life.
</p>
Database statistics データベース統計
<p> This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references. Currently, 6961 flavonoid structures, 0 plant species, and 0 references describing 19865 are registered.
</p>
Flavonoid content in food 食品中の量
| Category | Flavonol | Flavone | Flavan | Flavanone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Names | quercetin, kampferol, myricetin, isorhamnetin | apigenin, luteolin | catechin, epicatechin | |
| broccoli ブロッコリ | ★ | |||
| celery セロリ | ★★ | |||
| fava そら豆 | ★★ | |||
| hot pepper とうがらし | ★★ | |||
| onion たまねぎ | ★★(★) | |||
| parsley パセリ | ★★★ | |||
| peppermint ペパーミント | ★★ | |||
| spinach ほうれん草 | ★ | |||
| thyme タイム | ★★★ | |||
| watercress クレソン | ★ | |||
| dill, fennel ディル、フェンネル | ★★★ |
★ 5 to <10 mg/100 g; ★★ 10 to <50 mg/100 g; ★★★ 50< mg/100 g
<p>
The following vegetables and herbs have flavonoid contents less than 5 mg/100 g:
beets, kidney beans, snap beans, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, cucumber, endive, gourd, leek, lettuce, green peas, sweet pepper, potato, radish, tomato, oregano, perrilla, rosemary
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.