Category:FL
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
{{#DEF:NumberOfSpecies|{{#countTitle:.+|Species}}}} | {{#DEF:NumberOfSpecies|{{#countTitle:.+|Species}}}} | ||
{{#DEF:NumberOfReferences|{{#expr:{{#countTitle:.+|Reference}}-{{#countTitle:^Country|Reference}} }} }} | {{#DEF:NumberOfReferences|{{#expr:{{#countTitle:.+|Reference}}-{{#countTitle:^Country|Reference}} }} }} | ||
| − | {{#DEF:NumberOfRelations|{{#countLine:^&& | + | {{#DEF:NumberOfRelations|{{#countLine:^&&_+&&FL|Reference}}}} |
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 7 October 2008
Flavonoid (フラボノイド)
Related Pages : Molecule Index : Author Index
Contents |
Class Overview
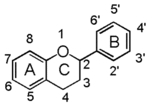
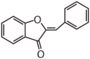
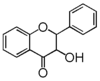
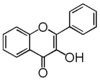
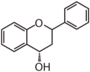
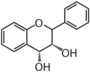
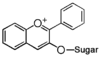
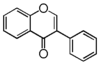
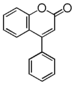
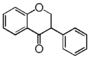
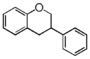
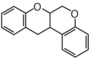
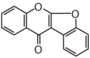
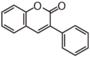
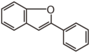
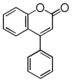
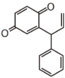
The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin flavus (yellow) with oid, meaning yellow-ish. It is probably due to its function as (yellow) flower pigments. Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).
The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan (tea), and isoflavone.
Links to familiar names 耳にする名前
- catechin in tea (お茶のカテキン)
- anthocyanin in berries (ベリーのアントシアニン)
- rutin in buckwheat (ソバのルチン)
- hesperidin in orange (ミカンのヘスペリジン)
- naringenin chalcone in tomato (トマトのナリンゲニンカルコン)
Biosynthesis 生合成
Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life.
Database statistics/ranking データベース統計
This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references. Currently, 6961 flavonoid structures, 3961 plant species, and 5215 references describing total 0 metabolite-species relationships are registered.
Flavonoid RanKING
- Heavy 重い
Heavenly blue anthocyanin ... Well-known skyblue pigment of morning glory (空色で有名な朝顔の色素)
- Light 軽い
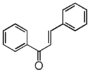
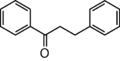
1,3-Diphenylpropan-1-one ... close to the amino acid Tryptophan (アミノ酸トリプトファンと同じぐらい)
- Long word (単語が)長い
isopropenyldihydrofuranoflavanone,
glucopyranosyldihydrokaempferol
- Long name (名前が)長い
Flavonoid content in food 食品中の量
| Category | Flavonol | Flavone | Flavan | Flavanone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Names | quercetin, kampferol, myricetin, isorhamnetin | apigenin, luteolin | catechin, epicatechin | |
| broccoli ブロッコリ | Δ | |||
| celery セロリ | ΔΔ | |||
| fava そら豆 | ΔΔ | |||
| hot pepper とうがらし | ΔΔ | |||
| onion たまねぎ | ΔΔ (Δ) | |||
| parsley パセリ | ΔΔΔ | |||
| peppermint ペパーミント | ΔΔ | |||
| spinach ほうれん草 | Δ | |||
| thyme タイム | ΔΔΔ | |||
| watercress クレソン | Δ | |||
| dill, fennel ディル, フェンネル | ΔΔΔ |
Δ 5 to <10 mg/100 g; ΔΔ 10 to <50 mg/100 g; ΔΔΔ 50< mg/100 g
The following vegetables and herbs have flavonoid contents less than 5 mg/100 g: beets, kidney beans, snap beans, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, cucumber, endive, gourd, leek, lettuce, green peas, sweet pepper, potato, radish, tomato, oregano, perrilla, rosemary
Design of Flavonoid ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| F | L | x | x | y | y | z | z | w | c | c | c |
- x ... backbone structure (母核構造)
FL1 aurone and chalcone; FL2 flavanone; FL3 flavone; FL4 Dihydroflavonol; FL5 Flavonol; FL6 Flavan; FL7 Anthocyanin; FLI Isoflavonoid; FLN Neoflavonoid
- y ... hydroxylation pattern in A and B ring (水酸基パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- z ... glycosylation pattern (糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- w ... halogenation etc. (ハロゲン等)
Currently unused.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.