Category:FL
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
{{#count:{{#searchline:&&FLI|Reference}}}}, | {{#count:{{#searchline:&&FLI|Reference}}}}, | ||
{{#count:{{#searchline:&&FLN|Reference}}}}| | {{#count:{{#searchline:&&FLN|Reference}}}}| | ||
| − | + | FL1,FL2,FL3,FL4,FL5,FL6,FL7,FLI,FLN|Relative number of identification reports}} | |
<br> | <br> | ||
==Familiar examples== | ==Familiar examples== | ||
anthocyanin (blueberry), isoflavone (soybean), rutin (soba noodle), catechin (tea), flavan-diol (tea), naringeninchalcone (tomato), polyphenol (wine, cacao) | anthocyanin (blueberry), isoflavone (soybean), rutin (soba noodle), catechin (tea), flavan-diol (tea), naringeninchalcone (tomato), polyphenol (wine, cacao) | ||
Revision as of 00:26, 17 March 2008
Contents |
FL: Flavonoid
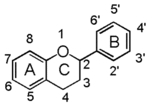
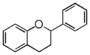
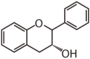
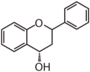
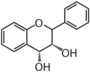
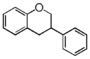
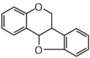
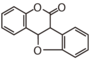
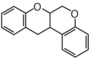
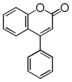
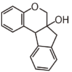
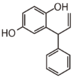
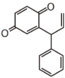
Flavonoid is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
| 1st Class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
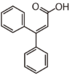
FL1:Aurone and Chalcone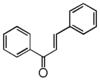
|
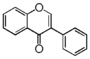
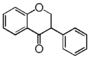
FL2:Flavanone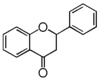
|
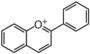
FL3:Flavone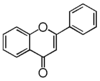
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FL2F: Flavanone | FL3F: Flavone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FL4: Dihydroflavonol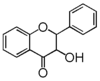
|
FL5: Flavonol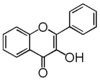
|
FL6: Flavan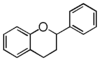
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FL4D: Dihydroflavonol | FL5F: Flavonol |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FL7: Anthocyanin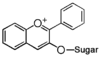
|
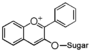
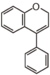
FLI: Isoflavonoid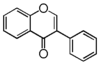
|
FLN: Neoflavonoid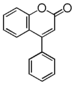
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biosynthesis
Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life.
Records in this database
This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references.
Familiar examples
anthocyanin (blueberry), isoflavone (soybean), rutin (soba noodle), catechin (tea), flavan-diol (tea), naringeninchalcone (tomato), polyphenol (wine, cacao)
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.