Category:FL
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | <!--- Class Information | + | <!--- Class Information (It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) |
| − | &&FL&&Flavonoid | + | &&FL&&Flavonoid&& |
| − | &&FL1&&Aurone and Chalcone | + | &&FL1&&Aurone and Chalcone&& |
| − | &&FL2&&Flavanone | + | &&FL1A&&Aurone&& |
| − | &&FL3&&Flavone | + | &&FL1B&&Auronol&& |
| − | &&FL4&&Dihydroflavonol | + | &&FL1C&&Chalcone&& |
| − | &&FL5&&Flavonol | + | &&FL1D&&Dihydrochalcone&& |
| − | &&FL6&&Flavan | + | &&FL2&&Flavanone&& |
| − | &&FL7&&Anthocyanin | + | &&FL3&&Flavone&& |
| − | &&FLI&&Isoflavonoid | + | &&FL4&&Dihydroflavonol&& |
| − | &&FLN&&Neoflavonoid | + | &&FL5&&Flavonol&& |
| + | &&FL6&&Flavan&& | ||
| + | &&FL63&&Flavan 3-ol&& | ||
| + | &&FL64&&Flavan 4-ol&& | ||
| + | &&FL6D&&Flavan 3,4-diol&& | ||
| + | &&FL7&&Anthocyanin&& | ||
| + | &&FL7A&&Anthocyanin&& | ||
| + | &&FL7D&&3-Desoxyanthocyanin&& | ||
| + | &&FLI&&Isoflavonoid&& | ||
| + | &&FLIA&&Isoflavone&& | ||
| + | &&FLIB&&Isoflavanone&& | ||
| + | &&FLIC&&Isoflavan&& | ||
| + | &&FLID&&Pterocarpane&& | ||
| + | &&FLIE&&Coumestan&& | ||
| + | &&FLIF&&Rotenoid&& | ||
| + | &&FLIG&&Coumaranochromone&& | ||
| + | &&FLIH&&3-Arylcoumarin&& | ||
| + | &&FLII&&2-Arylbenzofuran&& | ||
| + | &&FLIJ&&alpha-Methoxynbenzoin&& | ||
| + | &&FLN&&Neoflavonoid&& | ||
| + | &&FLNA&&4-Arylcoumarin&& | ||
| + | &&FLNB&&4-Arylchroman&& | ||
| + | &&FLNC&&Dalbergiquinol&& | ||
| + | &&FLND&&Dalbergione&& | ||
| + | &&FLNE&&Neoflavene&& | ||
| + | &&FLNF&&Coumarinic acid&& | ||
---> | ---> | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 9 March 2008
FL: Flavonoid
Structural Characteristics
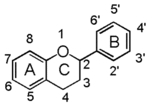
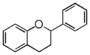
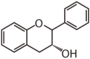
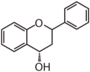
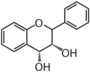
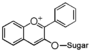
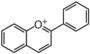
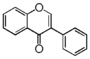
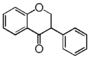
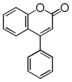
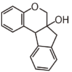
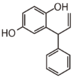
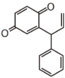
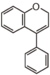
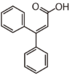
Flavonoid is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
| 1st Class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FL1:Aurone and Chalcone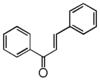
|
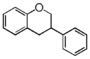
FL2:Flavanone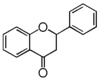
|
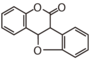
FL3:Flavone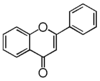
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FL4: Dihydroflavonol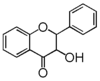
|
FL5: Flavonol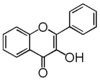
|
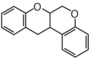
FL6: Flavan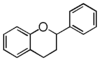
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FL7: Anthocyanin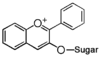
|
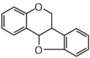
FLI: Isoflavonoid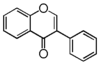
|
FLN: Neoflavonoid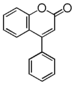
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biosynthesis
Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life.
Familiar examples.
anthocyanin (blueberry), isoflavone (soybean), rutin (soba noodle), catechin (tea), flavan-diol (tea), naringeninchalcone (tomato), polyphenol (wine, cacao)
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.