Category:FL
(→Biodiversity) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Class Overview== | ==Class Overview== | ||
| − | { | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" |
| + | ! Explanation (解説) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<p> | ||
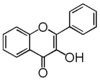
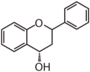
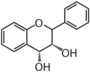
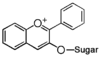
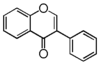
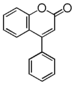
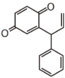
The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin ''flavus'' (yellow) with ''oid'', meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See [[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]). Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). | The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin ''flavus'' (yellow) with ''oid'', meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See [[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]). Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). | ||
The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1). | The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1). | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone. | Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone. | ||
| − | | | + | </p> |
| + | |<p> | ||
フラボノイドの語源は,ラテン語の flavus (黄色)に「~のような」という意味の oid をつけたものです。これは代表的なフラボンであるquercetinやkaempferolが広く使われてきた黄色の天然色素であることに由来しています ([[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]参照)。 | フラボノイドの語源は,ラテン語の flavus (黄色)に「~のような」という意味の oid をつけたものです。これは代表的なフラボンであるquercetinやkaempferolが広く使われてきた黄色の天然色素であることに由来しています ([[:Category:FL3F|flavone]]参照)。 | ||
| Line 18: | Line 22: | ||
フラボノイドの用途は 色素から食品添加物まで多様です。 よく耳にするものでは, アントシアニン, カテキン, フラバン(茶), イソフラボンなど, 全てフラボノイドです。 | フラボノイドの用途は 色素から食品添加物まで多様です。 よく耳にするものでは, アントシアニン, カテキン, フラバン(茶), イソフラボンなど, 全てフラボノイドです。 | ||
| − | + | </p> | |
| + | |} | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 77: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |align="center"|[[:Category:FL7|FL7: | + | |align="center"|[[:Category:FL7|FL7: Anthocyani(di)n]]<br>アントシアニ(ジ)ン<br>[[Image:Fl7.png|100px]]<br>purple vegetables/fruits<br>(赤)紫の野菜、果物 |
|align="center"|[[:Category:FLI|FLI: Isoflavonoid]]<br>イソフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fli.png|100px]]<br>beans<br>豆類 | |align="center"|[[:Category:FLI|FLI: Isoflavonoid]]<br>イソフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fli.png|100px]]<br>beans<br>豆類 | ||
|align="center"|[[:Category:FLN|FLN: Neoflavonoid]]<br>ネオフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fln.png|75px]] | |align="center"|[[:Category:FLN|FLN: Neoflavonoid]]<br>ネオフラボノイド<br>[[Image:Fln.png|75px]] | ||
| Line 180: | Line 185: | ||
==Biosynthesis 生合成== | ==Biosynthesis 生合成== | ||
| − | { | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" |
| − | Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life. | + | ! Explanation (解説) |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life. | ||
| | | | ||
| − | 一般にポリフェノール類は | + | <!----一般にポリフェノール類は |
# フェニルプロパノイド経路 から生合成されるもの と | # フェニルプロパノイド経路 から生合成されるもの と | ||
# 酢酸-マロン酸経路 から生合成されるもの | # 酢酸-マロン酸経路 から生合成されるもの | ||
にわかれます。 たとえば, 1 では、クマリン, リグナン, リグニンなどが生合成され, 2 の酢酸-マロン酸経路では, アントラキノンが知られています。 | にわかれます。 たとえば, 1 では、クマリン, リグナン, リグニンなどが生合成され, 2 の酢酸-マロン酸経路では, アントラキノンが知られています。 | ||
フラボノイドは, 上記 2 つの, 脂肪酸フェニルプロパノイド経路と 酢酸-マロン酸パスウェイとの 組み合わせにより生合成されます。 同様のパスウェイから生成される産物には, キサントン, スチルベンなどがあります。 | フラボノイドは, 上記 2 つの, 脂肪酸フェニルプロパノイド経路と 酢酸-マロン酸パスウェイとの 組み合わせにより生合成されます。 同様のパスウェイから生成される産物には, キサントン, スチルベンなどがあります。 | ||
| − | + | -----> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| style="text-align:center" | {| style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 4-coumaroyl CoA + malonyl CoA | + | | 4-coumaroyl CoA<br/>+ malonyl CoA |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]CHS | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]CHS | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | chalcone | + | | [[:Category:FL1|''chalcone'']] |
| | | | ||
| − | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL2|FLAVONES]] | + | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL2|''FLAVONES'']] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]CHI | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]CHI | ||
| Line 229: | Line 216: | ||
| colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| quercetin | | colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| quercetin | ||
| colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| myricetin | | colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| myricetin | ||
| − | | colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| [[:Category:FL5|FLAVONOLS]] | + | | colspan="2" style="background:lavender"| [[:Category:FL5|''FLAVONOLS'']] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]F3H | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]F3H | ||
| Line 243: | Line 230: | ||
| style="background:mistyrose"| dihydro-myricetin | | style="background:mistyrose"| dihydro-myricetin | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL4|DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS]] | + | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL4|''DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS'']] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]DFR | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]DFR | ||
| Line 259: | Line 246: | ||
| style="background:lavender"| leuco-delphinidin | | style="background:lavender"| leuco-delphinidin | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | style="background:lavender"| LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS | + | | style="background:lavender"| [[:Category:FL6|''LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS'']] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]ANS | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]ANS | ||
| Line 269: | Line 256: | ||
| style="background:mistyrose"| delphinidin | | style="background:mistyrose"| delphinidin | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL7|ANTHO-CYANIDINS]] | + | | style="background:mistyrose"| [[:Category:FL7|''ANTHO-CYANIDINS'']] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]UR3GT | | [[Image:Arrow00d35.png]]UR3GT | ||
| Line 279: | Line 266: | ||
| style="background:lavender"| delphinidin 3-glucoside | | style="background:lavender"| delphinidin 3-glucoside | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | style="background:lavender"| [[:Category:FL7|ANTHO-CYANINS]] | + | | style="background:lavender"| [[:Category:FL7|''ANTHO-CYANINS'']] |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Bioactivity== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''all flavonoids''' | ||
| + | ''photoprotectant, anti-oxidant'' <br/> | ||
| + | Not only anthocyanins but even simple structures such as chalcone can absorb UV wavelengths strongly. The ability of photoprotection is derived from its anti-oxidative activity. For example, quercetin is a more effective photoprotectant and anti-oxidant than kaempferol <ref name="Ryan 2002">Ryan KG, Swinny EE, Markham KR, Winefield C: Flavonoid gene expression and UV photoprotection in transgenic and mutant Penunia leaves. Phytochem 2002 59:23-32</ref>. | ||
| + | |'''全フラボノイド''' | ||
| + | ''抗紫外線、抗酸化作用'' <br/> | ||
| + | アントシアニンだけでなく、カルコンのような構造の簡単なフラボノイドでも紫外線をよく吸収します。効紫外線は効酸化作用に由来します。例えばクエルセチンはケンフェロールよりも強い効紫外線、効酸化作用を示します<ref name="Ryan 2002"/>。 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Tannins (proanthocyanidins)''' | ||
| + | ''anti-bacteria, anti-fungi'' | ||
| + | |'''タンニン (プロアントシアニジニン)''' | ||
| + | ''抗菌、抗カビ作用'' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Biosynthesis== | ||
| + | * Flavonoids are seen only in land plants (not algae). | ||
| + | |||
==Database statistics/ranking データベース統計== | ==Database statistics/ranking データベース統計== | ||
Revision as of 23:32, 21 September 2009
Flavonoid (フラボノイド)
| Flavonoid Top | Molecule Index | Author Index | Journals | Structure Search | Food | New Input |
Contents |
Class Overview
| Explanation (解説) | |
|---|---|
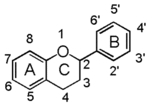
The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin flavus (yellow) with oid, meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See flavone). Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).
The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone. |
フラボノイドの語源は,ラテン語の flavus (黄色)に「~のような」という意味の oid をつけたものです。これは代表的なフラボンであるquercetinやkaempferolが広く使われてきた黄色の天然色素であることに由来しています (flavone参照)。 化学的な定義でフラボノイドとは, ベンゼン環2個 (それぞれA環B環と呼ばれる) を3つの炭素 (C) で結合した, 植物の代謝産物の総称です (Figure 1)。 Figure 1 において 2,3,4 と番号付けされた炭素鎖は A 環の水酸基と結合して C 環を構成します。フラボノイドのカテゴリーは,たいてい C 環の修飾パターンで決まります (Table 1)。 フラボノイドの用途は 色素から食品添加物まで多様です。 よく耳にするものでは, アントシアニン, カテキン, フラバン(茶), イソフラボンなど, 全てフラボノイドです。 |
Links to familiar names 耳にする名前
- isoflavonoid in beans (豆のイソフラボン)
- anthocyanin in berries (ベリーのアントシアニン)
- catechin in tea (お茶のカテキン)
- rutin in buckwheat (ソバのルチン)
- hesperidin in orange (ミカンのヘスペリジン)
- naringenin chalcone in tomato (トマトのナリンゲニンカルコン)
Biosynthesis 生合成
| Explanation (解説) | |
|---|---|
| Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life. |
| 4-coumaroyl CoA + malonyl CoA | |||||||||
| | |||||||||
| chalcone | FLAVONES | ||||||||
| |
/FS | ||||||||
| naringenin | kaempferol | quercetin | myricetin | FLAVONOLS | |||||
| |
/ FLS | / FLS | / FLS | ||||||
| dihydro-kaempferol | F3'H |
dihydro-quercetin | F3'5'H |
dihydro-myricetin | DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS | ||||
| |
\LCR | LCR/ | |
LCR/ | | ||||
| leuco-pelargonidin | PROANTHO- CYANIDINS | leuco-cyanidin | PROANTHO- CYANIDINS | leuco-delphinidin | LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS | ||||
| |
|
| |||||||
| pelargonidin | cyanidin | delphinidin | ANTHO-CYANIDINS | ||||||
| |
|
| |||||||
| pelargonidin 3-glucoside | cyanidin 3-glucoside | delphinidin 3-glucoside | ANTHO-CYANINS | ||||||
Bioactivity
| all flavonoids
photoprotectant, anti-oxidant |
全フラボノイド
抗紫外線、抗酸化作用 |
| Tannins (proanthocyanidins)
anti-bacteria, anti-fungi |
タンニン (プロアントシアニジニン)
抗菌、抗カビ作用 |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ryan KG, Swinny EE, Markham KR, Winefield C: Flavonoid gene expression and UV photoprotection in transgenic and mutant Penunia leaves. Phytochem 2002 59:23-32
Biosynthesis
- Flavonoids are seen only in land plants (not algae).
Database statistics/ranking データベース統計
This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references. Currently, 6961 flavonoid structures, 3961 plant species, and 5215 references describing total 19861 metabolite-species relationships are registered.
Some Flavonoid Ranking ちょっとしたランキング
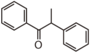
- Heavy 重い
Heavenly blue anthocyanin ... Well-known skyblue pigment of morning glory (空色で有名な朝顔の色素)
- Light 軽い
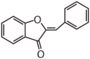
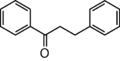
1,3-Diphenylpropan-1-one ... as light as the amino acid Tryptophan (アミノ酸トリプトファンと同じぐらいの軽さ)
- Long word (単語が)長い
isopropenyldihydrofuranoflavanone,
glucopyranosyldihydrokaempferol
- Long name (名前が)長い
Flavonoid content in food 食品中の量
| Category | Flavonol | Flavone | Flavan | Flavanone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Names | quercetin, kampferol, myricetin, isorhamnetin | apigenin, luteolin | catechin, epicatechin | |
| broccoli ブロッコリ | Δ | |||
| celery セロリ | ΔΔ | |||
| fava そら豆 | ΔΔ | |||
| hot pepper とうがらし | ΔΔ | |||
| onion たまねぎ | ΔΔ (Δ) | |||
| parsley パセリ | ΔΔΔ | |||
| peppermint ペパーミント | ΔΔ | |||
| spinach ほうれん草 | Δ | |||
| thyme タイム | ΔΔΔ | |||
| watercress クレソン | Δ | |||
| dill, fennel ディル, フェンネル | ΔΔΔ |
Δ 5 to <10 mg/100 g; ΔΔ 10 to <50 mg/100 g; ΔΔΔ 50< mg/100 g
The following vegetables and herbs have flavonoid contents less than 5 mg/100 g: beets, kidney beans, snap beans, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, cucumber, endive, gourd, leek, lettuce, green peas, sweet pepper, potato, radish, tomato, oregano, perrilla, rosemary
Design of Flavonoid ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| F | L | x | x | y | y | z | z | w | c | c | c |
- x ... backbone structure (母核構造)
FL1 aurone and chalcone; FL2 flavanone; FL3 flavone; FL4 Dihydroflavonol; FL5 Flavonol; FL6 Flavan; FL7 Anthocyanin; FLI Isoflavonoid; FLN Neoflavonoid
- y ... hydroxylation pattern in A and B ring (水酸基パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- z ... glycosylation pattern (糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- w ... halogenation etc. (ハロゲン等)
Currently unused.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
For Users of Flavonoid Viewer
The flavonoid IDs used in this site is the same as those in Flavonoid Viewer in metabolome.jp except for the following FL7 category.
| Anthocyanin glycosylated with other than glucose and galactose | ||
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid Viewer FL7A..GS |
→ | This site FL7A..GO |
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.