Category:FL
m (→{{Bilingual|フラボノイドの概要|Class Overview}}) |
|||
| Line 174: | Line 174: | ||
---> | ---> | ||
| − | + | {{Category:FL/Biosynthesis}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=={{Bilingual|生物活性|Bioactivity}}== | =={{Bilingual|生物活性|Bioactivity}}== | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 7 January 2011
Flavonoid Database
| Flavonoid Top | Molecule Index | Author Index | Journals | Structure Search | Food | New Input |
Contents |
Class Overview
The word "flavonoid" comes from its Latin origin flavus (yellow) with oid, meaning yellow-ish. It comes from its history as yellow natural dye (quercetin and kaempferol are the most widespread flavone dyes. See flavone).
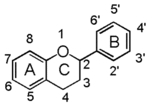
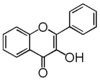
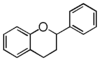
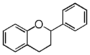
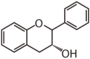
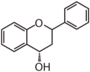
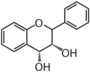
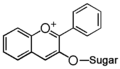
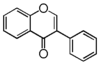
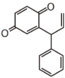
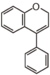
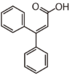
Chemically speaking, it is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1).
The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, is linked to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. The class of flavonoids are usually determined by the modification pattern of the C-ring (Table 1).
Flavonoid is utilized in many industrial processes from pigments to food additives. Often heard names include anthocyanin, catechin, flavan, and isoflavone.
| 1st Class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
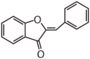
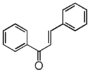
| FL1: Anthochlor (Aurone and Chalcone) |
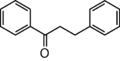
FL2: Flavanone |
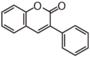
FL3: Flavone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
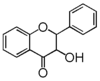
| FL4: Dihydroflavonol |
FL5: Flavonol |
FL6: Flavan (Leucoanthocyanidin) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FL7: Anthocyani(di)n |
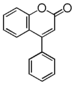
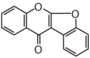
FLI: Isoflavonoid |
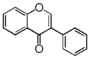
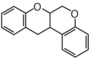
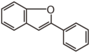
FLN: Neoflavonoid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biosynthesis of Flavonoid
Flavonoid is synthesized through both the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway and the acetate-malonate pathway in all higher plants (but not algae). Most plants contain the 6 major subgroups: chalcones, flavanones, flavones, flavonols, flavans, and anthocyani(di)ns. Aurones or isoflavonoids are not ubiquitous.
| 4-coumaroyl CoA + malonyl CoA | ||||||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||||
| CHALCONES, AURONES |
chalconaringenin |
FLAVONES |
apigenin |
luteolin | ||||||||||||
| CHI |
| |||||||||||||||
IFS |
naringenin FLAVANONE |
kaempferol |
FLAVONOLS |
quercetin |
myricetin | |||||||||||
| ISO-FLAVONES |
F3H |
|||||||||||||||
| DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS |
dihydro-kaempferol |
F3'H +OH in B-ring |
dihydro-quercetin |
F3'5'H +OH in B-ring |
dihydro-myricetin | |||||||||||
| DFR |
|
|
||||||||||||||
| LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS |
leuco-pelargonidin |
|
leuco-cyanidin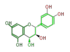
|
leuco-delphinidin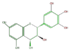
|
||||||||||||
| LDOX |
PROANTHO- CYANIDINS * | |
PROANTHO- CYANIDINS * | |
*...polymers of flavanols | |||||||||||
| ANTHO-CYANIDINS |
pelargonidin |
|
cyanidin |
|
delphinidin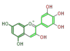
|
| ||||||||||
| UF3GT |
epi-afzelechin |
|
epi-catechin |
|
epigallo-catechin |
FLAVAN 3-OLS | ||||||||||
| ANTHO-CYANINS |
pelargonidin 3-glucoside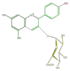
|
cyanidin 3-glucoside |
delphinidin 3-glucoside | |||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Information for the Above Abbreviated Gene Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Six Structural Genes | |||
| Abbrev. | Name | Origin | Information |
| CHS | chalcone synthase | Bacterial polyketide synthases, particularly those in fatty acid synthesis (Verwoert et al. 1992) | Early response against light [1] [2] |
| CHI | chalcone-flavanone isomerase | Unclear and unique to plants.[3]
Eubacterium ramulus has the CHI activity. [4] |
Early response against light. |
| F3H | flavanone 3-hydroxylase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family [5] | Early response in Arabidopsis but late in Antirrhinum [6] |
| FLS | flavonol synthase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family [7] | Early response against light. In Arabidopsis, all structural genes are single-copy except for this one, to which six genes exist and two of them are not expressed. |
| DFR | dihydroflavonol 4-reductase | NADPH-dependent reductase associated with steroid metabolism [8] | Later response |
| ANS/LDOX | anthocyanidin synthase or leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family | Later response |
| Auxiliary Genes | |||
| F3'H | flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family [9] | |
| F3'5'H | flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family [10] | Not reported in mosses or liverworts. The transformation of the F3'5'H and the cytochrome b5 gene of petunia into carnation changed its flower color deep purple.[11][12] |
| FSI | flavone synthase | Dioxygenase in parsley (FSI) and P450 monooxygenase in snapdragon (FSII). | |
| LAR (or LCR) | leucoanthocyanidin reductase | ||
| UF3GT | UDP flavonoid glucosyltransferase | ||
| GST | glutathione-S-transferase | Transport of flavonoids from cytoplasm to vacuole or cell walls requires both GST and the glutathione pump in ATP-binding cassette family.[13][14] | |
| AOMT | anthocyanin O-methyl transferase | ||
| |||
Evolutionary Pressure
Rausher and colleagues studied the relationship between pathway architecture and protein evolutionary rates in anthocyanin biosynthetic pathways. Upstream enzymes showed reduced rates of non-synonymous substitution compared with downstream enzymes, which are under relaxed constraints, in both broad (Zea in monocot and Antirrhinum and Ipomoea in eudicot [1] [2] ) and narrow (within Ipomoea [3]) comparisons. Similarly, the downstream enzyme is under less selective pressure in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway [4].
- ↑ Rausher MD, Miller R, Tiffin P (1999) "Patterns of evolutionary rate variation among genes of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway" Mol Biol Evol 16:266-274
- ↑ Lu Y, Rausher MD (2003) "Evolutionary rate variation in anthocyanin pathway genes" Mol Biol Evol 20:1844-1853
- ↑ Rausher MD, Lu Y, Meyer K (2008) "Variation in constraint versus positive selection as an explanation for evolutionary rate variation among anthocyanin genes" J Mol Evol 7:137-144
- ↑ Livingstone K, Anderson S (2009) "Patterns of variation in the evolution of carotenoid biosynthetic pathway enzymes of higher plants" J Heredity 100:754-761
Bioactivity
Tea Related
- Tea category 茶の種類
- Tea consumption 茶の消費量
- Tea and health 茶と健康
Others
- Photoprotectant, anti-oxidant activity (More Information)
Not only anthocyanins but even simple structures such as chalcone can absorb UV wavelengths strongly. The ability of photoprotection is derived from its anti-oxidative activity.
- Hypotensive activity
Quercetin in onions and flavanols in cocoa are said to reduce blood pressure in hypertensive animals [1], but their effect or mechanism is not clinically conclusive.
- ↑ Hooper L, Kroon PA, Rimm EB, et al. (2008) "Flavonoids, flavonoid-rich foods, and cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials" Am J Clin Nutr 88:38–50 PMID 18614722
- Anti-bacteria, anti-fungal activity
Tannins (proanthocyanidins) show anti-bacterial activity.
Database statistics/ranking
This database collects original references that report identification of flavonoid in various plant species. The database consists of three major namespaces: (flavonoid) compounds, plant species, and references. Currently, 6961 flavonoid structures, 3961 plant species, and 5215 references describing total 19861 metabolite-species relationships are registered.
| class | FL1 (chalcones) |
FL2 (flavanones) |
FL3 (flavones) |
FL4 (dihydroflavonols) |
FL5 (flavonols) |
FL6 (flavans) |
FL7 (anthocyanidins) |
FLI (isoflavonoids) |
FLN (neoflavonoids) |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #data | 690 | 705 | 1479 | 272 | 1943 | 291 | 574 | 916 | 96 | 6961 |
Flavonoid content in food
For details, please visit this page.
- Food containing high Flavanone
Flavanones are rich in citrus, not in vegetables.
| Food | Flavanone (mg/100g) |
食品名 |
|---|---|---|
| grapefruit, raw or juice | 14-53 | グレープフルーツ (生、ジュース) |
| orange and tangerine, raw or juice | 13-33 | オレンジ、みかん (生、ジュース) |
- Food containing high flavone
Many herbs contain flavones. Parsley is rich in apigenin; celery and thyme in luteolin.
| Food | Flavone (mg/100g) |
食品名 |
|---|---|---|
| celery hearts, raw | 19 | セロリの芯 (生) |
| parsley, raw | 302 | パセリ (生) |
- Food containing high flavonol
Flavonols are prevalent in vegetables, usually in small amounts. Onions, kales, hot peppers are good sources.
| Food | Flavonol (mg/100g) |
食品名 |
|---|---|---|
| buckwheat | 23 | そば |
| cranberry, juice | 16 | クランベリー (ジュース) |
| onion, raw or boiled | 5-20 | たまねぎ (生、ゆで等) |
| kale, raw or canned | 18-34 | ケール (生、かんづめ) |
- Food containing high flavan
Catechins and epicatechins are contained in legumes and teas, but not in other vegetables.
| Food | Flavan (mg/100g or 100ml) |
食品名 |
|---|---|---|
| broadbeans, raw | ~50 | そらまめ (生) |
| dark chocolate bar | ~50 | ダークチョコレート |
| black grapes | 18 | 黒いブドウ |
| brewed black tea | > 16 | 淹れた紅茶 |
| brewed oolong tea | 50 | 淹れたウーロン茶 |
| brewed green tea | > 50 | 淹れた緑茶 |
- Food containing high anthocyanin
Anthocyanins are contained in berries. Vegetables supply only small amounts.
| Food | Anthocyanin (mg/100g) |
食品名 |
|---|---|---|
| blueberries, raw | 113 | ブルーベリー (生) |
| sweet cherries, raw | 116 | さくらんぼ (生) |
| elderberries, raw | 749 | エルダーベリー (生) |
| raspberries, raw | 49 | ラズベリー (生) |
- Vegetables and herbs with scarce flavonoids
The following vegetables and herbs have flavonoid contents less than 5 mg/100 g: beets, kidney beans, snap beans, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, cucumber, endive, gourd, leek, lettuce, green peas, sweet pepper, potato, radish, tomato, oregano, perrilla, rosemary
Design of Flavonoid ID numbers
12-DIGIT
| F | L | x | x | y | y | z | z | w | c | c | c |
- x ... backbone structure (母核構造)
FL1 aurone and chalcone; FL2 flavanone; FL3 flavone; FL4 Dihydroflavonol; FL5 Flavonol; FL6 Flavan; FL7 Anthocyanin; FLI Isoflavonoid; FLN Neoflavonoid
- y ... hydroxylation pattern in A and B ring (水酸基パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- z ... glycosylation pattern (糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details. General description is here.
- w ... halogenation etc. (ハロゲン等)
Currently unused.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
For Users of Flavonoid Viewer
The flavonoid IDs used in this site is the same as those in Flavonoid Viewer in metabolome.jp except for the following FL7 category.
| Anthocyanin glycosylated with other than glucose and galactose | ||
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid Viewer FL7A..GS |
→ | This site FL7A..GO |
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.