Category:TP3
Contents |
Triterpene (C30) Biosynthesis
Triterpenes are formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. The precursor compound of cholesterol (C27) is lanosterol (C30) for animals. For plants, fungi and algae, it is almost cycloartenol with a trace of lanosterol-derived sterols[1].
Steroid
Ring configuration
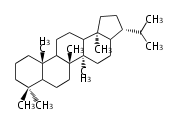
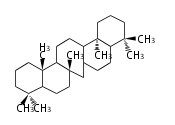
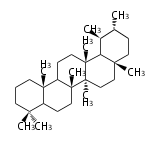
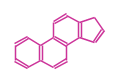
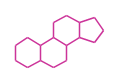
The basic steroid structure is 4 carbon rings, cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, gonane, or sterane. The rings B/C are always trans in all natural steroids. If the rings C/D are trans, it is called gonane. If its stereochemistry is unspecified, it is called sterane. Most steroids take gonane form, but in cardenolides and bufanolides, the rings C/D are cis.
 |
|
| Cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | Gonane |
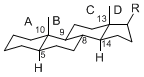
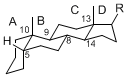
The majority of steroids have methyl groups sticking out from the bridgehead positions C-10 and C-13. When these methyl groups (or hydrogens) stand above the plane, they are called β-configuration. Those below the plane are called α-configuration. If the configuration at any site is unknown, it is indicated as ξ (Greek Xi). By default, hydrogen atoms or substituents at the positions C-8, 9, 10, 13, and 14 are assumed to be 8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, and 14α configurations. C-5 is a special position, because there are as many 5α steroids as 5β are.
 |
|
| 5α-configuration | 5β-configuration |
Hormonal Classes
Estranes (C18)
The backbone of estrogens, the hormones responsible for female reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics. The original spelling was 'oestrogen'. Major namings are:
- estrogen ... estra-1,3,5(10)-triene
- estrone ... 3-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-17-one
- estradiol ... estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol
- estriol ... estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol
- equine estrogens ... estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraene and estra-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene series
Androstanes (C19)
The backbone of male hormone testosterones. Major namings are:
- etianic acids (C20) ... androstane-17-carboxylic acids and their derivatives
- D-homoandrostanes (C20) ... ring D is expanded by including C-17a carbon.
Pregnanes (C21)
The backbone of pregnancy hormone progesterone and the majority of corticosteroids. It is the largest single group of steroids. Major namings are:
- progesterone ... pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
- 17α-ethynylandrostane ... 17α-pregn-20-yne
- 19-norpregnane (C20) ... 17α-ethynylestrane, 19-nor-17α-pregn-20-yne
Cholanes (C24)
The backbone of bile acids, i.e., 5β-cholan-24-oic acids with hydroxyl substitution at C-3.
- primary bile acids ... cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are biosynthesized directly from cholesterol.
- secondary bile acids ... deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid are generated by intestinal bacteria.
- 24-norcholan-23-oic acids ... loss of one carbon side chain
- 23,24-dinorcholan-22-oic acids ... loss of two carbon side chains
C/D cis Classes
Cardenolides (C23)
The backbone of Digitalis glycosides with the androstane skeleton with a γ-lactone ring at C-17. Notable characters are its 14β-configuration in opposition to other steroids (the rings C/D are cis), and the 20(22)-double bond. Their cardiac activity is well known.
Bufanolides (C24)
The backbone of toad skin secretions and the sea onion or squill (Scilla maritima) with a δ-lactone ring at C-17. As for cardenolides, 14β, 17β, and 20R-configurations are assumed (the rings C/D are cis). They naturally occur as glycosides or conjugates of suberylarginine.
Steroidal Classes
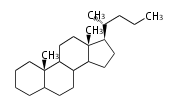
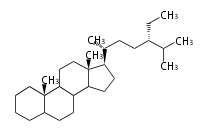
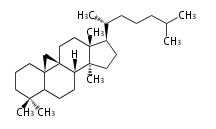
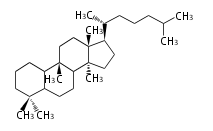
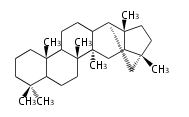
Sterols (C27)
The sterol backbone contains a β hydroxyl group at C-3 and side chains of 8-10 carbons at C-17. They are important membrane constituents in addition to their biologically activity.
Major categories are:
- cholestane ... androstane structure with a branched C8 chain at the 17β-position
- norcholestane ... cholestane lacking one of 27 carbons
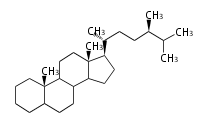
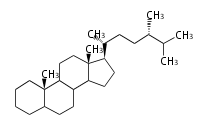
- ergostane and campestane ... 24β- and 24α-methylcholestane
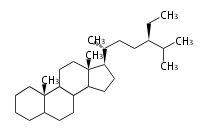
- poriferastane and stigmastane ... 24β- and 24α-ethylcholestane
- vitamin D2 ... 9,10-secoergonstane derivatives
- vitamin D3 ... 9,10-secocholestane derivatives
- lumistane ... 9β,10α-ergosta-5,7-diene
Ecdysteroid (C27)
Ecdysteroids (or ecdysones) are moulting hormones of insects and crustaceans, but also present in many plants. The basic skeleton is highly oxygenated cholestane: 2β,3β,14α,20,22-pentahydroxy-5β-cholest-7-en-6-one. The first ecdysteroid to be isolated was α-ecdysone from teh silkworm (Bombyx mori).
Spirostans and furostans (C27)
Furostan has the additional epoxy ring E. Spirostan has another epoxy ring F, which is perpendicular to the planar orientation of rings A-E. The omission of a terminal 'e' from spirostans and furostans indicates that they are not hydrocarbons.
(However, the last 'e' is needed if a consonant follows.)
Major categories are:
- furostan ... 16β,22-epoxycholestane
- spirostan ... 22,26-epoxyfurostan
Withanolides (C28)
Withanolides were found in the root of Withania Somnifera, also known as Indian ginseng. Its backbone is a highly oxygenated ergostane with a γ-lactone ring linking C-22 and C-26 [2]. The configuration of C-22 is usually R.
Brassinolides (C28)
Brassinolides are plant growth-promoting hormones isolated originally from Brassica napus (rape). Its backbone is a highly oxygenated ergostane with the oxygen-expanded B-ring (ε-lactone). This lactone is not essential for plant growth activity (e.g. castasterone) but the 22R, 23R-diol are. The configurations of C-2,3 and 5 are α in brassinolides whereas they are β in ecdysteroids.
Gorgostane (C30)
Gorgostanes occur in marine organisms. Its backbone is ergostane with an additional metyl group at C-23 and ana methylene bridge between C-22 and C-23.
Biosynthesis
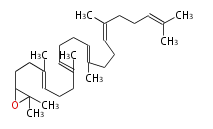 2,3-Oxidosqualene |
|
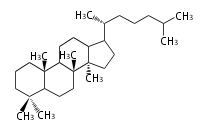 ダンマラン (dammarane) 型 |
| | ||
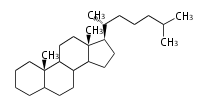 Cholestane-type |
|
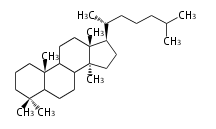 Lanostane-type |
| | ||
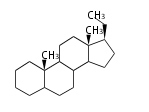 Pregnane-type |
|
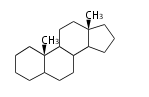 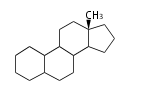 Androstane- and Estrane-type |
Phytosterols
Most common phytosterols are campesterol, β-sitosterol, and stigmasterol. Soybean (Glycine max, Fabaceae) is a rich source of phytosterols (about 0.1% of its weight), and is used for semi-synthesis of medicinal steroids [3]. Since dietary phytosterols reduce cholesterol levels, they are used as food additives such as for margarine [4]. Vitamin D is a family of sterol metabolites generated photochemically in our skin by UV irradiation.
Saponins
Saponins are surfactant glycosides, i.e., they produce foams in aqueous solution and therefore are called ‘sapo’ (a Latin for soap). Plant-based crude drugs are still actively prescribed in Eastern Asia, and many of their active components are attributed to saponins. Well known examples of saponin and its aglycone include glycyrrhizin from liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis/glabra, Category:Fabaceae) used in European confectionery and Asian medicine; ginsenosides from ginseng (Panax ginseng, Araliaceae) for tonic, especially in Korea; diosgenin from wild yam (Dioscorea spp., Dioscoreaceae) for hormone replacement therapy.
 2,3-Oxidosqualene |
|
 ダンマラン (dammarane) 型 |
| | ||
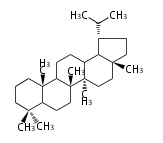 Lupane-type |
|
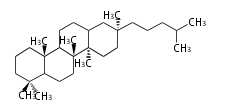 Baccharane-type |
| | ||
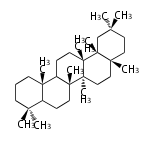 Oleanane-type |
|
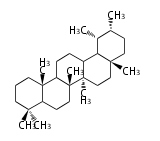 Taraxastane-type |
Design of Tri-terpene ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| T | P | 3 | x | y | y | r | h | g | n | c | c |
- x ... species information
| Symbol at x | Kingdom | Phyla | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Animalia | Arthropoda (Insects, crabs) | ecdysteroids |
| V | Chordate (Vertebrates) | sex steroids, corticosteroids, anabolic steroids | |
| O | Others | marine steroids | |
| P | Plantae | Phytosterols | lanosterols, cholesterols, brassinolides |
| S | Saponins | saponins | |
| F | Fungi | ergosterols | ergosterols |
| B | Bacteria | bacterial sterols | hopanoids |
- y ... backbone structure (母核構造)
|
- r ... number of major rings (環構造数)
Click above categories to see details.
- h ... hydroxylation pattern (水酸基数)
Click above categories to see details.
- g ... glycosylation pattern(糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details.
- n ... number of sugars (修飾糖数)
Click above categories to see details.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
This category currently contains no pages or media.