Category:FL7A
| (5 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | {{Hierarchy|{{PAGENAME}}}} | ||
| + | =={{Bilingual|アントシアニンの概要|Overview}}== | ||
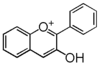
| + | '''{{Bilingual|アントシアニジン|Anthocyanidins}}''' | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | + | Anthocyanidins are the flavonoid backbone of anthocyanins without glycosylation (called aglycon). The 6 most common anthocyanidins are: | |
| − | + | [[FL7AAANS0001|pelargonidin]], [[FL7AACNS0001|cyanidin]], [[FL7AAGNS0001|delphinidin]], [[FL7AADNS0001|peonidin]], [[FL7AAHNS0001|petunidin]], and [[FL7AAINS0001|malvidin]]. | |
| − | + | They are conjugated with sugars, hydroxycinnamates, and organic acids such as acetate. | |
| − | + | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | アントシアニンの糖がついていない状態(アグリコンと呼びます)をアントシアニジンと呼びます。 | |
| − | + | 基本となる骨格は[[FL7AAANS0001|ペラルゴニジン]]、[[FL7AACNS0001|シアニジン]]、[[FL7AAGNS0001|デルフィニジン]]、[[FL7AADNS0001|ペオニジン]]、[[FL7AAHNS0001|ペチュニジン]]、[[FL7AAINS0001|マルビジン]]の7種で、これらに糖や桂皮酸、酢酸などの有機酸が付加されてアントシアニンとなります。 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{FL_digit56|FL7A}} | {{FL_digit56|FL7A}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:27, 19 August 2010
Anthocyanin
| Flavonoid Top | Molecule Index | Author Index | Journals | Structure Search | Food | New Input |
Upper classes : FL Flavonoid : FL7 Anthocyani(di)n
Contents |
[edit] Overview
Anthocyanidins
Anthocyanidins are the flavonoid backbone of anthocyanins without glycosylation (called aglycon). The 6 most common anthocyanidins are: pelargonidin, cyanidin, delphinidin, peonidin, petunidin, and malvidin. They are conjugated with sugars, hydroxycinnamates, and organic acids such as acetate.
[edit] Major Plant Families
|
|
The number in each family is counted as the number of genera (not species) listed in our registered references. Each reference record is accessible by clicking the link in compound pages. The taxonomy follows the APG-II classification. For details (or if the figure is broken), visit this page. 各科のカウントは種名でなく文献に記載された属名の数です。文献は代謝物ページのリンクからたどれ、分類はAPG-IIです。左の図が表示されない場合はここをクリックしてください。 |
[edit] Patterns of Hydroxylation
| Category Names in the 3rd Class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The 5th and 6th digits of our flavonoid ID indicates the hydroxylation patterns of A-ring and B-ring (See the upper-right figure. The leftmost ring is A, rightmost is B), respectively. The following chart is spanned by these 2 digits. R indicates H or CH3, and R' indicates H or R. Numbers are IUPAC positions. The value in each cell (such as GS: glycosilation only) corresponds to the 7th and 8th digits, which is explained at the bottom of this page.
|
Position of -OH (-OCH3) groups |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| A (104 pages) | B (0 pages) | C (177 pages) | D (41 pages) | E (0 pages) | F (0 pages) | G (116 pages) | H (35 pages) | I (62 pages) | J (0 pages) | K (0 pages) | L (0 pages) | 8 (0 pages) | 9 (0 pages) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (500 pages) | GA (8 pages) GL (76 pages) GO (6 pages) GS (6 pages) NS (1 pages) | CL (1 pages) DL (1 pages) GA (21 pages) GL (133 pages) GO (7 pages) GS (7 pages) NS (1 pages) | GA (3 pages) GL (29 pages) GO (3 pages) GS (3 pages) NS (1 pages) | GA (17 pages) GL (76 pages) GO (7 pages) GS (7 pages) NS (1 pages) | GA (1 pages) GL (24 pages) GO (3 pages) GS (3 pages) NS (1 pages) | GA (1 pages) GL (41 pages) GO (5 pages) GS (5 pages) NS (1 pages) | |||||||||
| B (12 pages) | GL (1 pages) NS (1 pages) | GL (1 pages) GO (1 pages) GS (1 pages) NS (1 pages) | GA (1 pages) GL (1 pages) NS (1 pages) | GO (1 pages) GS (1 pages) NS (1 pages) | |||||||||||
| C (6 pages) | GL (1 pages) NS (1 pages) | GL (3 pages) NS (1 pages) | |||||||||||||
| D (2 pages) | NS (2 pages) | ||||||||||||||
| E (11 pages) | GL (2 pages) NS (1 pages) | GL (3 pages) NS (1 pages) | GL (3 pages) NS (1 pages) | ||||||||||||
| F (4 pages) | GL (4 pages) | ||||||||||||||
| G (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
| 1 (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
| 2 (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
| 3 (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
| 4 (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
| 9 (0 pages) | |||||||||||||||
Abbreviations used in the above chart
- First Characters
N not glycosylated; G O-glycoside; C C-glycoside; D both glycosides;
- Second Characters
S not modified; M alkylated; I prenylated; R cyclic-prenylated; F furanoFL; P pyranoFL; D furano and pyranoFL; N phenylpropanoid; C others;
- Special Second Character only for Anthycyanin (FL7)
A Galactosylated; L Glucosylated; O modified with other sugars;
[edit] Other Unusual Patterns
These types are not classified in the above chart.
| Quinone | QU (0 pages) | alpha-Hydroxy | HX (0 pages) | beta-Hydroxy | HY (0 pages) | Peltogynoid | PT (0 pages) |
| Retrocalchone | RT (0 pages) | Dehydro-backbone | WX (0 pages) | Additional rings | RN (0 pages) | Others | UN (0 pages) |
| Pyranoanthocyanin (FL7 only) | RX (8 pages) | ||||||
[edit] Patterns of Glycosylation
The 7th and 8th digits of the flavonoid ID indicates the glycosylation, and other modification patterns, respectively. The following chart is spanned by these 2 digits. The value in each cell (such as AA for the standard form) corresponds to the 5th and 6th digits.
| 7th digit → 8th digit ↓ |
No glycosylation N (18 pages) | O-glycoside G (523 pages) | C-glycoside C (1 pages) | O- & C-glycoside D (1 pages) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| no modification | S (51 pages) | AA (1 pages) AC (1 pages) AD (1 pages) AG (1 pages) AH (1 pages) AI (1 pages) BC (1 pages) BG (1 pages) BH (1 pages) BI (1 pages) CD (1 pages) CI (1 pages) DI (2 pages) EA (1 pages) EC (1 pages) EG (1 pages) RX (1 pages) | AA (6 pages) AC (7 pages) AD (3 pages) AG (7 pages) AH (3 pages) AI (5 pages) BG (1 pages) BI (1 pages) | ||
| alkylated | M (0 pages) | ||||
| prenylated | I (0 pages) | ||||
| cyclic prenylated | R (0 pages) | ||||
| furano FL | F (0 pages) | ||||
| pyrano FL | P (0 pages) | ||||
| furano & pyrano FL | D (0 pages) | ||||
| prenylpropanoid | N (0 pages) | ||||
| others | C (0 pages) | ||||
| 3-Gal related | A | N.A. | AA (8 pages) AC (21 pages) AD (3 pages) AG (17 pages) AH (1 pages) AI (1 pages) BH (1 pages) | N.A. | N.A. |
| 3-Glc related | L | N.A. | AA (76 pages) AC (133 pages) AD (29 pages) AG (76 pages) AH (24 pages) AI (41 pages) BC (1 pages) BG (1 pages) BH (1 pages) CD (1 pages) CI (3 pages) EA (2 pages) EC (3 pages) EG (3 pages) FA (4 pages) RX (7 pages) | N.A. | N.A. |
| other sugar at 3 | O | N.A. | AA (6 pages) AC (7 pages) AD (3 pages) AG (7 pages) AH (3 pages) AI (5 pages) BG (1 pages) BI (1 pages) | N.A. | N.A. |
This category currently contains no pages or media.