Category:FL
From Metabolomics.JP
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
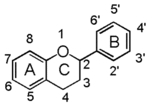
Flavonoid is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). [[Image:FL.gif|thumb|150px|right|Fig.1 The Backbone of Flavonoid Structure]] The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, can link to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. Flavonoid is structurally classified by the modification pattern of this C-ring. | Flavonoid is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). [[Image:FL.gif|thumb|150px|right|Fig.1 The Backbone of Flavonoid Structure]] The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, can link to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. Flavonoid is structurally classified by the modification pattern of this C-ring. | ||
| − | < | + | <table> |
| − | Image:Fl1c.gif|Chalcones and Aurones | + | <tr> |
| − | Image:Fl2.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fl1c.gif|thumb|150px|Chalcones and Aurones]]</td> |
| − | Image:Fl3.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fl2.gif|thumb|150px|Flavanone]]</td> |
| − | </ | + | <td>[[Image:Fl3.gif|thumb|150px|Flavone]]</td> |
| − | < | + | </tr> |
| − | Image:Fl4.gif| | + | <tr> |
| − | Image:Fl5.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fl4.gif|thumb|150px|Dihydroflavonol]]</td> |
| − | Image:Fl6.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fl5.gif|thumb|150px|Flavonol]]</td> |
| − | </ | + | <td>[[Image:Fl6.gif|thumb|150px|Flavan]]</td> |
| − | < | + | </tr> |
| − | Image:Fl7.gif| | + | <tr> |
| − | Image:Fli.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fl7.gif|thumb|150px|Anthocyanin]]</td> |
| − | Image:Fln.gif| | + | <td>[[Image:Fli.gif|thumb|150px|Isoflavonoid]]</td> |
| − | </ | + | <td>[[Image:Fln.gif|thumb|150px|Neoflavonoid]]</td> |
| + | </tr></table> | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 2 March 2008
Flavonoid
Flavonoid is a class of plant secondary metabolites that have two benzene rings (each called A-ring and B-ring) connected by a chain of three carbons (Figure 1). The carbon chain, corresponding to the numbers 2,3,4 in Figure 1, can link to a hydroxyl group in the A-ring to form the C-ring. Flavonoid is structurally classified by the modification pattern of this C-ring.File:Fl1c.gif Chalcones and Aurones |
File:Fl2.gif Flavanone |
File:Fl3.gif Flavone |
File:Fl4.gif Dihydroflavonol |
File:Fl5.gif Flavonol |
File:Fl6.gif Flavan |
File:Fl7.gif Anthocyanin |
File:Fli.gif Isoflavonoid |
File:Fln.gif Neoflavonoid |
Flavonoid is synthesized through the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway in all higher plants. It is responsible for many biological activities including pigments, anti-oxidative or anti-allergic agents, and signaling elements in nodule formation. Some of them are quite familiar in our daily life.
Familiar examples.
anthocyanin (blueberry), isoflavone (soybean), rutin (soba noodle), catechin (tea), flavan-diol (tea), naringeninchalcone (tomato), polyphenol (wine, cacao)
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.