Category:FL/Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of Flavonoid
Flavonoid is synthesized through both the phenylpropanoid-acetate pathway and the acetate-malonate pathway in all higher plants (but not algae). Most plants contain the 6 major subgroups: chalcones, flavanones, flavones, flavonols, flavans, and anthocyani(di)ns. Aurones or isoflavonoids are not ubiquitous.
| 4-coumaroyl CoA + malonyl CoA | ||||||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||||
| CHALCONES, AURONES |
chalconaringenin |
FLAVONES |
apigenin |
luteolin | ||||||||||||
| CHI |
| |||||||||||||||
IFS |
naringenin FLAVANONE |
kaempferol |
FLAVONOLS |
quercetin |
myricetin | |||||||||||
| ISO-FLAVONES |
F3H |
|||||||||||||||
| DIHYDRO FLAVONOLS |
dihydro-kaempferol |
F3'H +OH in B-ring |
dihydro-quercetin |
F3'5'H +OH in B-ring |
dihydro-myricetin | |||||||||||
| DFR |
|
|
||||||||||||||
| LEUCOANTHO-CYANIDINS |
leuco-pelargonidin |
|
leuco-cyanidin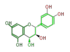
|
leuco-delphinidin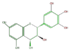
|
||||||||||||
| LDOX |
PROANTHO- CYANIDINS * | |
PROANTHO- CYANIDINS * | |
*...polymers of flavanols | |||||||||||
| ANTHO-CYANIDINS |
pelargonidin |
|
cyanidin |
|
delphinidin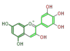
|
| ||||||||||
| UF3GT |
epi-afzelechin |
|
epi-catechin |
|
epigallo-catechin |
FLAVAN 3-OLS | ||||||||||
| ANTHO-CYANINS |
pelargonidin 3-glucoside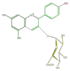
|
cyanidin 3-glucoside |
delphinidin 3-glucoside | |||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Information for the Above Abbreviated Gene Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Six Structural Genes | |||
| Abbrev. | Name | Origin | Information |
| CHS | chalcone synthase | Bacterial polyketide synthases, particularly those in fatty acid synthesis (Verwoert et al. 1992) | Early response against light [1] [2] |
| CHI | chalcone-flavanone isomerase | Unclear and unique to plants.[3]
Eubacterium ramulus has the CHI activity. [4] |
Early response against light. |
| F3H | flavanone 3-hydroxylase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family [5] | Early response in Arabidopsis but late in Antirrhinum [6] |
| FLS | flavonol synthase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family [7] | Early response against light. In Arabidopsis, all structural genes are single-copy except for this one, to which six genes exist and two of them are not expressed. |
| DFR | dihydroflavonol 4-reductase | NADPH-dependent reductase associated with steroid metabolism [8] | Later response |
| ANS/LDOX | anthocyanidin synthase or leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase | 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family | Later response |
| Auxiliary Genes | |||
| F3'H | flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family [9] | |
| F3'5'H | flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase | cytochrome P450 hydroxylase family [10] | Not reported in mosses or liverworts. The transformation of the F3'5'H and the cytochrome b5 gene of petunia into carnation changed its flower color deep purple.[11][12] |
| FSI | flavone synthase | Dioxygenase in parsley (FSI) and P450 monooxygenase in snapdragon (FSII). | |
| LAR (or LCR) | leucoanthocyanidin reductase | ||
| UF3GT | UDP flavonoid glucosyltransferase | ||
| GST | glutathione-S-transferase | Transport of flavonoids from cytoplasm to vacuole or cell walls requires both GST and the glutathione pump in ATP-binding cassette family.[13][14] | |
| AOMT | anthocyanin O-methyl transferase | ||
| |||
Evolutionary Pressure
Rausher and colleagues studied the relationship between pathway architecture and protein evolutionary rates in anthocyanin biosynthetic pathways. Upstream enzymes showed reduced rates of non-synonymous substitution compared with downstream enzymes, which are under relaxed constraints, in both broad (Zea in monocot and Antirrhinum and Ipomoea in eudicot [1] [2] ) and narrow (within Ipomoea [3]) comparisons. Similarly, the downstream enzyme is under less selective pressure in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway [4].
- ↑ Rausher MD, Miller R, Tiffin P (1999) "Patterns of evolutionary rate variation among genes of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway" Mol Biol Evol 16:266-274
- ↑ Lu Y, Rausher MD (2003) "Evolutionary rate variation in anthocyanin pathway genes" Mol Biol Evol 20:1844-1853
- ↑ Rausher MD, Lu Y, Meyer K (2008) "Variation in constraint versus positive selection as an explanation for evolutionary rate variation among anthocyanin genes" J Mol Evol 7:137-144
- ↑ Livingstone K, Anderson S (2009) "Patterns of variation in the evolution of carotenoid biosynthetic pathway enzymes of higher plants" J Heredity 100:754-761
This category currently contains no pages or media.