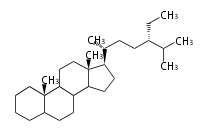
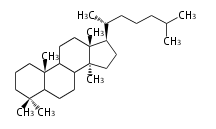
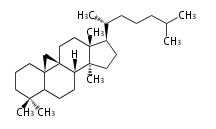
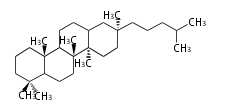
Category:TP3
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ==Triterpene (C30) Biosynthesis== | + | ==Triterpene (C30) Classes== |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Biosynthesis== | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
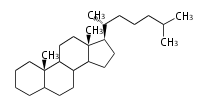
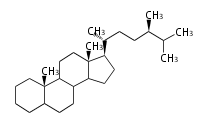
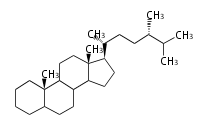
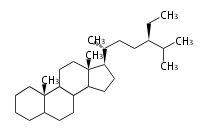
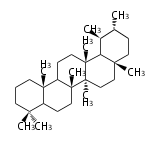
Triterpenes are formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. The precursor compound of cholesterol (C27) is lanosterol (C30) for animals. For plants, fungi and algae, it is almost cycloartenol with a trace of lanosterol-derived sterols<ref>Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T “Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3):725-730, 2009</ref>. | Triterpenes are formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. The precursor compound of cholesterol (C27) is lanosterol (C30) for animals. For plants, fungi and algae, it is almost cycloartenol with a trace of lanosterol-derived sterols<ref>Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T “Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(3):725-730, 2009</ref>. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 9: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | ==Ring configuration== | ||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
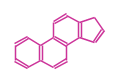
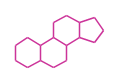
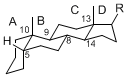
| + | The basic structure is 4 carbon rings, cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, gonane, or sterane. | ||
| + | The rings B/C are always ''trans'' in all natural steroids. If the rings C/D are ''trans'', it is called gonane. If its stereochemistry is unspecified, it is called sterane. | ||
| + | Most steroids take gonane form, but in cardenolides and bufanolides, the rings C/D are ''cis''. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | 基本骨格は4つの環構造で、シクロペンタ[a]フェナンスレン、ゴナン、ステランなどと呼ばれます。 | ||
| + | 天然のステロイドでは環 B/C は常にトランスの位置にあります。 | ||
| + | 環 C/D がトランスの場合をゴナン、立体配置が指定されていないときをステランと呼びます。 | ||
| + | ほとんどのステロイドはゴナンの形をとりますが、カルデノライドとブファノライドは環 C/D がシスになります。 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | | [[Image:Cyclopenta-a-phenanthrene.png]] || [[Image:Gonane.png]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | ||
| + | | Gonane | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| − | |||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
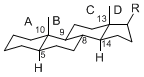
| − | + | The majority of steroids have methyl groups sticking out from the bridgehead positions C-10 and C-13. | |
| + | When these methyl groups (or hydrogens) stand above the plane, they are called β-configuration. | ||
| + | Those below the plane are called α-configuration. If the configuration at any site is unknown, it is indicated as ξ (Greek Xi). | ||
| + | By default, hydrogen atoms or substituents at the positions C-8, 9, 10, 13, and 14 are assumed to be | ||
| + | 8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, and 14α configurations. C-5 is a special position, because there are as many 5α steroids as 5β are. | ||
| | | | ||
| + | 大多数のステロイドは橋頭位のC-10, C-13からメチル基が出ます。 | ||
| + | これらのメチル基 (または水素など) が平面より上に出ているときを、ベータ配置とします。平面より下の場合がアルファ配置です。 | ||
| + | 配置が不明な場合は、ξ (ギリシャ語の Xi)で表します。 | ||
| + | 原則として、C-8, 9, 10, 13, 14位にある水素や置換基はそれぞれ8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, 14α 配置です。 | ||
| + | C-5位だけは特別で、5α のステロイドと 5β のものが同じくらい存在するので指定が必要です。 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | | [[Image:5alpha-steroid.png]] || [[Image:5beta-steroid.png]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5α-configuration | ||
| + | | 5β-configuration | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
Revision as of 12:07, 3 August 2010
Contents |
Triterpene (C30) Classes
Biosynthesis
Triterpenes are formed by joining two FPPs tail-to-tail. The precursor compound of cholesterol (C27) is lanosterol (C30) for animals. For plants, fungi and algae, it is almost cycloartenol with a trace of lanosterol-derived sterols[1].
Ring configuration
The basic structure is 4 carbon rings, cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene, gonane, or sterane. The rings B/C are always trans in all natural steroids. If the rings C/D are trans, it is called gonane. If its stereochemistry is unspecified, it is called sterane. Most steroids take gonane form, but in cardenolides and bufanolides, the rings C/D are cis.
 |
|
| Cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | Gonane |
The majority of steroids have methyl groups sticking out from the bridgehead positions C-10 and C-13. When these methyl groups (or hydrogens) stand above the plane, they are called β-configuration. Those below the plane are called α-configuration. If the configuration at any site is unknown, it is indicated as ξ (Greek Xi). By default, hydrogen atoms or substituents at the positions C-8, 9, 10, 13, and 14 are assumed to be 8β, 9α, 10β, 13β, and 14α configurations. C-5 is a special position, because there are as many 5α steroids as 5β are.
 |
|
| 5α-configuration | 5β-configuration |
Design of Tri-terpene ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| T | P | 3 | x | y | y | r | h | g | n | c | c |
- x ... species information
| Symbol at x | Kingdom | Phyla | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Animalia | Arthropoda (Insects, crabs) | ecdysteroids |
| V | Chordate (Vertebrates) | sex steroids, corticosteroids, anabolic steroids | |
| O | Others | marine steroids | |
| P | Plantae | Phytosterols | lanosterols, cholesterols, brassinolides |
| S | Saponins | saponins | |
| F | Fungi | ergosterols | ergosterols |
| B | Bacteria | bacterial sterols | hopanoids |
- y ... backbone structure (母核構造)
|
- r ... number of major rings (環構造数)
Click above categories to see details.
- h ... hydroxylation pattern (水酸基数)
Click above categories to see details.
- g ... glycosylation pattern(糖修飾パターン)
Click above categories to see details.
- n ... number of sugars (修飾糖数)
Click above categories to see details.
- c ... serial number (通し番号)
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
This category currently contains no pages or media.