Category:FL1
(→Carthamin (カルタミン)) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
===Carthamin (カルタミン)=== | ===Carthamin (カルタミン)=== | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | The oldest known chalcone is [[en:carthamin|Carthamin]] from safflower (''[[Species:Carthamus|Carthamus tinctorius]]''), a crimson dye that has long been used in India, Egypt, Japan, and other countries. Major pigments in safflower are water-soluble [[FL1CQUCS0001|Safflor yellow A]], Safflomin A, Safflomin B and [[FL1CQUCN0001|Safflomin C]] (60%). On the other hand, red Carthamin, which is water-insoluble, is only less than 1%. The structure of Carthamin, two chalcones connected by a methine group, was identified | + | The oldest known chalcone is [[en:carthamin|Carthamin]] from safflower (''[[Species:Carthamus|Carthamus tinctorius]]''), a crimson dye that has long been used in India, Egypt, Japan, and other countries. Major pigments in safflower are water-soluble [[FL1CQUCS0001|Safflor yellow A]], Safflomin A, Safflomin B and [[FL1CQUCN0001|Safflomin C]] (60%). On the other hand, red Carthamin, which is water-insoluble, is only less than 1% <ref>Obara H., Onodera J., Sato S. "Carthamin, the Red Pigment of Safflower" ''Bull. Yamagata Univ. 22(2), 1993 [http://repo.lib.yamagata-u.ac.jp/bitstream/123456789/1215/1/kiyoue-22-2-02.html (in Japanese)]</ref>. The structure of Carthamin, two chalcones connected by a methine group, was identified in 1979<ref>Obara H., Onodera J. "Structure of Carthamin", ''Chem. Lett'' 201-204, 1979 |
| + | </ref>. This is why we do not have Carthamin in this database, which collects only chalcone monomers. The same is true for Safflomin B, whose structure is a coupling of two chalcones. | ||
| | | | ||
一番古くから知られるカルコンはおそらく, 紅花の赤色色素[[ja:carthamin|カルタミン]]でしょう。 | 一番古くから知られるカルコンはおそらく, 紅花の赤色色素[[ja:carthamin|カルタミン]]でしょう。 | ||
インド、エジプト、日本をはじめ多くの国で利用されてきました。紅花の色素は大半が水溶性の | インド、エジプト、日本をはじめ多くの国で利用されてきました。紅花の色素は大半が水溶性の | ||
[[FL1CQUCS0001|サフラワーイエローA]], サフロミン A, サフロミン B そして [[FL1CQUCN0001|サフロミン C]]です。 | [[FL1CQUCS0001|サフラワーイエローA]], サフロミン A, サフロミン B そして [[FL1CQUCN0001|サフロミン C]]です。 | ||
| − | カルタミンは水に不溶で1%にすぎません。その構造は2つのカルコンがメチン基で結合しており, | + | カルタミンは水に不溶で1%にすぎません。その構造は2つのカルコンがメチン基で結合しており, 1979年に山形大学の小野寺らが明らかにしました。このデータベースではカルコンの単体しか収録していないため |
| − | カルタミンは含まれていません。サフロミン Bも二つのカルコンが結合した構造のため、収録していません。 | + | カルタミンは含まれていません。サフロミン Bも二つのカルコンが結合した構造のため、収録していません。 |
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <references/> | ||
==Database statistics データベース統計== | ==Database statistics データベース統計== | ||
Revision as of 10:44, 8 January 2010
Aurone, Auronol, Chalcone, and Dihydrochalcone
| Flavonoid Top | Molecule Index | Author Index | Journals | Structure Search | Food | New Input |
Upper classes : FL Flavonoid
| Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FL1A | Aurone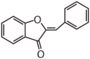
|
FL1B | Auronol |
| FL1C | Chalcone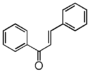
|
FL1D | Dihydrochalcone |
Chalcones and aurones are called anthochlor (chlōros means yellow in Greek). When flowers with anthochlor are fumed with ammonia, they turn to red. Anthochlors are found in at least Caryophyllaceae, Compositae, Rosaceae, and Scrophulariaceae. Aurones are oxidized forms of chalcones and usually both exist together in yellow flowers. Chalcones, unlike aurones, occur sporadically in other parts of plants.
Carthamin (カルタミン)
The oldest known chalcone is from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius), a crimson dye that has long been used in India, Egypt, Japan, and other countries. Major pigments in safflower are water-soluble Safflor yellow A, Safflomin A, Safflomin B and Safflomin C (60%). On the other hand, red Carthamin, which is water-insoluble, is only less than 1% [1]. The structure of Carthamin, two chalcones connected by a methine group, was identified in 1979[2]. This is why we do not have Carthamin in this database, which collects only chalcone monomers. The same is true for Safflomin B, whose structure is a coupling of two chalcones.
- ↑ Obara H., Onodera J., Sato S. "Carthamin, the Red Pigment of Safflower" Bull. Yamagata Univ. 22(2), 1993 (in Japanese)
- ↑ Obara H., Onodera J. "Structure of Carthamin", Chem. Lett 201-204, 1979
Database statistics データベース統計
Major Plant Families
|
|
The number in each family is counted as the number of genera (not species) listed in our registered references. Each reference record is accessible by clicking the link in compound pages. The taxonomy follows the APG-II classification. For details (or if the figure is broken), visit this page. 各科のカウントは種名でなく文献に記載された属名の数です。文献は代謝物ページのリンクからたどれ、分類はAPG-IIです。左の図が表示されない場合はここをクリックしてください。 |