Category:FL1
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | + | Chalcones and aurones are called ''anthochlor'' (chlōros means yellow in Greek). When flowers with anthochlor are fumed with ammonia, they turn to red. Anthochlors are found in at least Caryophyllaceae, Compositae, Rosaceae, and Scrophulariaceae. Aurones are oxidized forms of chalcones and usually both exist together in yellow flowers. Chalcones, unlike aurones, occur sporadically in other parts of plants. | |
| + | | | ||
| + | カルコンとオーロンは、''アントクロール''(クロールとはギリシャ語で黄色)と呼ばれます。これらの色素はアンモニアでアルカリにすると赤色になります。アントクロールはナデシコ科、キク科、バラ科、ゴマノハグサ科に見られます。オーロンはカルコンが酸化してできるため通常は両方が黄色花に両方が含まれます。ただ、オーロンと違ってカルコンは花以外の場所に見られる場合があります。 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Carthamin (カルタミン)=== | ||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| + | The oldest known chalcone is [[en:carthamin|Carthamin]] from safflower (''[[Species:Carthamus|Carthamus tinctorius]]''), a crimson dye that has long been used in India, Egypt, Japan, and other countries. Major pigments in safflower are water-soluble [[FL1CQUCS0001|Safflor yellow A]], Safflomin A, Safflomin B and [[FL1CQUCN0001|Safflomin C]] (60%). On the other hand, red Carthamin, which is water-insoluble, is only less than 1%. The structure of Carthamin, two chalcones connected by a methine group, was identified by Onodera et al. in 1979. (This is why we do not have Carthamin in this database, which collects only chalcone monomers. The same is true for Safflomin B, whose structure is a coupling of two chalcones.) | ||
| | | | ||
一番古くから知られるカルコンはおそらく, 紅花の赤色色素[[ja:carthamin|カルタミン]]でしょう。 | 一番古くから知られるカルコンはおそらく, 紅花の赤色色素[[ja:carthamin|カルタミン]]でしょう。 | ||
Revision as of 14:17, 1 April 2009
Aurone, Auronol, Chalcone, and Dihydrochalcone
| Flavonoid Top | Molecule Index | Author Index | Journals | Structure Search | Food | New Input |
Upper classes : FL Flavonoid
| Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FL1A | Aurone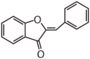
|
FL1B | Auronol |
| FL1C | Chalcone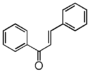
|
FL1D | Dihydrochalcone |
Chalcones and aurones are called anthochlor (chlōros means yellow in Greek). When flowers with anthochlor are fumed with ammonia, they turn to red. Anthochlors are found in at least Caryophyllaceae, Compositae, Rosaceae, and Scrophulariaceae. Aurones are oxidized forms of chalcones and usually both exist together in yellow flowers. Chalcones, unlike aurones, occur sporadically in other parts of plants.
Carthamin (カルタミン)
The oldest known chalcone is from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius), a crimson dye that has long been used in India, Egypt, Japan, and other countries. Major pigments in safflower are water-soluble Safflor yellow A, Safflomin A, Safflomin B and Safflomin C (60%). On the other hand, red Carthamin, which is water-insoluble, is only less than 1%. The structure of Carthamin, two chalcones connected by a methine group, was identified by Onodera et al. in 1979. (This is why we do not have Carthamin in this database, which collects only chalcone monomers. The same is true for Safflomin B, whose structure is a coupling of two chalcones.)
- Obara H., Onodera J. "Structure of Carthamin", Chem. Lett 201-204, 1979
- Obara H., Onodera J., Sato S. "Carthamin, the Red Pigment of Safflower" Bull. Yamagata Univ. 22(2), 1993 (in Japanese)
Database statistics データベース統計