Category:TP3S
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==Saponins== | ==Saponins== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| + | Saponins are glycosides of lipophilic steroids (C27) or triterpenoids (C30) in plant. | ||
| + | Since sugars are water-soluble, they function as surfactant, i.e., they produce foams in aqueous solution and therefore are called ‘sapo’ (a Latin for soap). | ||
| + | The foams cause haemolysis of blood erythrocytes and saponins are toxic to cold-blooded animals (but not to warm-blooded ones). They are also toxic to insects and molluscs. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| + | Saponins are often present as a mixture of similar glycosides (4 or 5 sugars are common) of one or more backbone structures (sapogenins). | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | + | Plant-based crude drugs are still actively prescribed in Eastern Asia, and many of their active components are attributed to saponins. Well known examples of saponin and its aglycone include glycyrrhizin from liquorice ([[Species:Glycyrrhiza|''Glycyrrhiza uralensis/glabra'']], [[:Category:Fabaceae]]) used in European confectionery and Asian medicine; ginsenosides from ginseng ([[Species:Panax|''Panax ginseng'']], [[:Category:Araliaceae|Araliaceae]]) for tonic, especially in Korea; diosgenin from wild yam ([[Species:Dioscorea|''Dioscorea spp.'']], [[:Category:Dioscoreaceae|Dioscoreaceae]]) for hormone replacement therapy. | |
| | | | ||
Latest revision as of 12:19, 3 August 2010
[edit] Saponins
Saponins are glycosides of lipophilic steroids (C27) or triterpenoids (C30) in plant. Since sugars are water-soluble, they function as surfactant, i.e., they produce foams in aqueous solution and therefore are called ‘sapo’ (a Latin for soap). The foams cause haemolysis of blood erythrocytes and saponins are toxic to cold-blooded animals (but not to warm-blooded ones). They are also toxic to insects and molluscs.
Saponins are often present as a mixture of similar glycosides (4 or 5 sugars are common) of one or more backbone structures (sapogenins).
Plant-based crude drugs are still actively prescribed in Eastern Asia, and many of their active components are attributed to saponins. Well known examples of saponin and its aglycone include glycyrrhizin from liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis/glabra, Category:Fabaceae) used in European confectionery and Asian medicine; ginsenosides from ginseng (Panax ginseng, Araliaceae) for tonic, especially in Korea; diosgenin from wild yam (Dioscorea spp., Dioscoreaceae) for hormone replacement therapy.
[edit] Biosynthesis
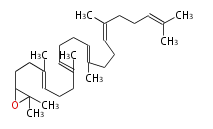 2,3-Oxidosqualene |
|
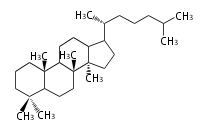 ダンマラン (dammarane) 型 |
| | ||
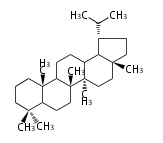 Lupane-type |
|
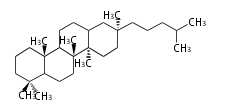 Baccharane-type |
| | ||
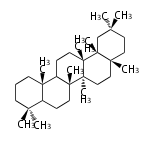 Oleanane-type |
|
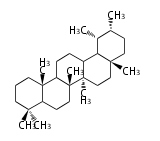 Taraxastane-type |
This category currently contains no pages or media.