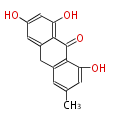
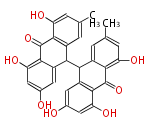
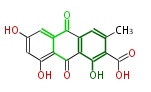
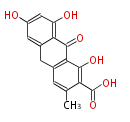
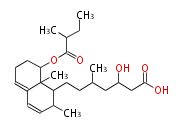Category:PK
m (→Polyketide Synthase (PKS)) |
m (→Polyketide Synthase (PKS)) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=={{Bilingual|概要|Overview}}== | =={{Bilingual|概要|Overview}}== | ||
| + | ==={{Bilingual|構造|Structure}}=== | ||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
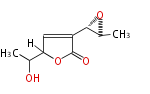
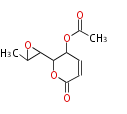
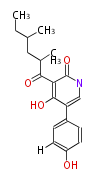
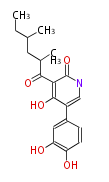
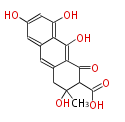
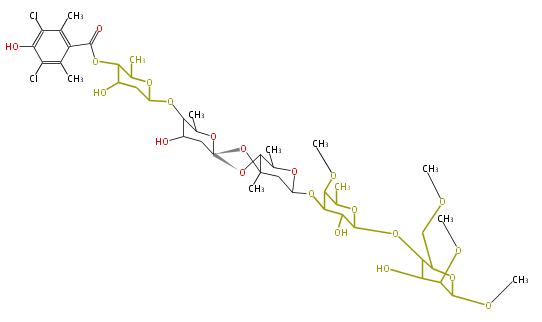
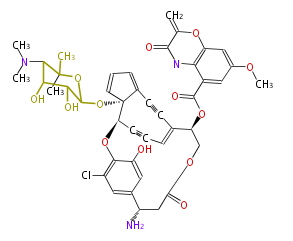
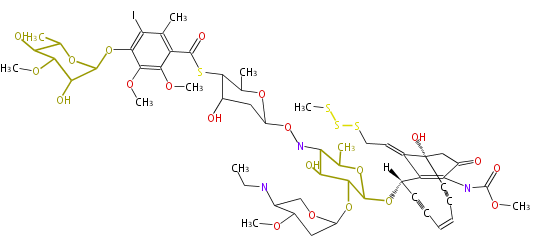
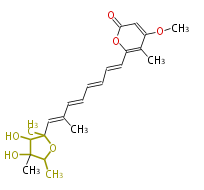
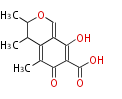
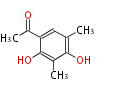
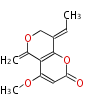
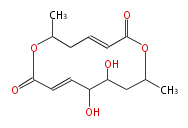
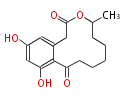
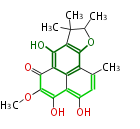
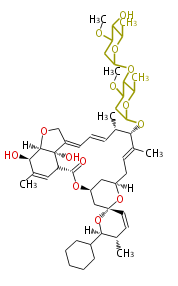
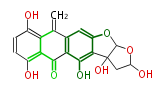
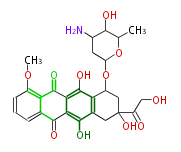
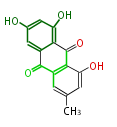
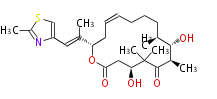
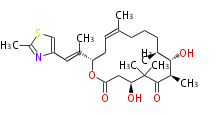
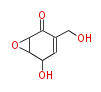
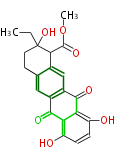
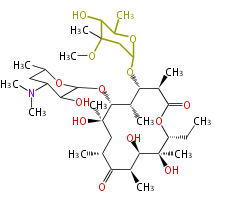
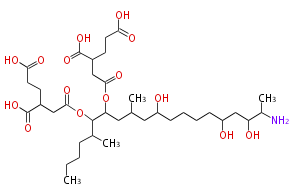
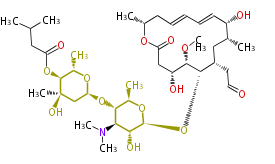
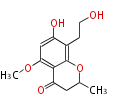
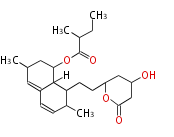
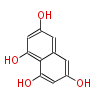
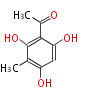
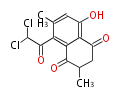
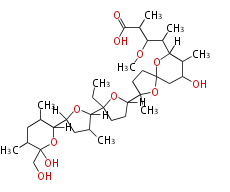
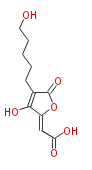
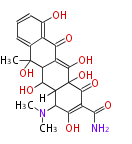
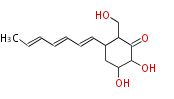
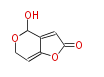
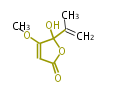
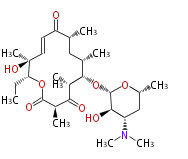
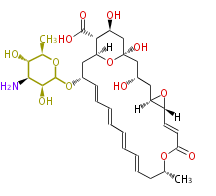
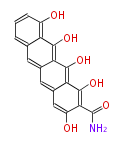
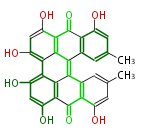
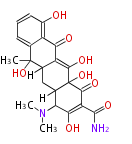
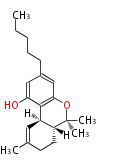
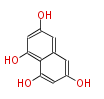
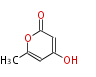
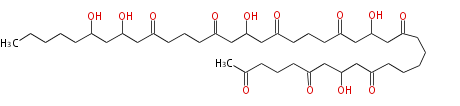
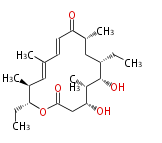
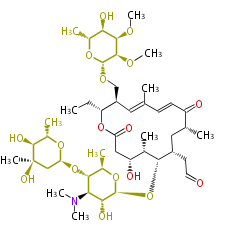
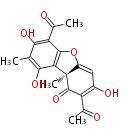
| + | Polyketides are natural products with multiple ketone structures and synthesized from acetyl CoA. The synthetic pathway is called Acetate-Malonate Pathway. | ||
| + | Well known products include erythromycin (antibiotic), melanin (pigment), and aflatoxin (toxin). | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ポリケチドはケトン構造を複数持つ天然物のカテゴリーで、アセチルCoAから作られます。その生合成ステップは、酢酸-マロン酸経路と呼ばれています。代表例は抗生物質のエリスロマイシン、色素のメラニン、毒素のアフラトキシンです。 | ||
| + | }} | ||
==={{Bilingual|酢酸-マロン酸経路|Acetate-Malonate Pathway}}=== | ==={{Bilingual|酢酸-マロン酸経路|Acetate-Malonate Pathway}}=== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 62: | ||
| + | <!--- | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
===3-4th digits=== | ===3-4th digits=== | ||
| − | + | Antimycin | |
Elfamycin | Elfamycin | ||
Kijanimicin | Kijanimicin | ||
Sorbicillin polymers | Sorbicillin polymers | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 249: | Line 256: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | ----> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Polyketide Synthase (PKS)= | ||
| − | + | =={{Bilingual|分布|Distribution}}== | |
| − | + | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
PKS members are found in bacteria, fungi, plants, slime mold<ref>Zucko J, Skunca N, Curk T, Zupan B, Long PF et al (2007) "Polyketide synthase genes and the natural products potential of Dictyostelium discoideum" ''Bioinformatics'' 23:2543-49</ref>, Alveolata<ref>Zhu G, LaGier MJ, Stejskal F, Millership JJ, Cai X et al (2002) "Cryptosporidium parvum: the first protist known to encode a putative polyketide synthase" ''Gene'' 298:79-89</ref>, and animals <ref>Castoe TA, Stephens T, Noonan BP, Calestani C (2007) "A novel group of type I polyketide synthases (PKS) in animals and the complex phylogenomics of PKSs" ''Gene'' 392:47-58</ref><ref>Calestani C, Rast JP, Davidson EH (2003) "Isolation of pigment cell specific genes in the sea urchin embryo by differential macroarray screening" ''Development'' 130:4587-96</ref>. | PKS members are found in bacteria, fungi, plants, slime mold<ref>Zucko J, Skunca N, Curk T, Zupan B, Long PF et al (2007) "Polyketide synthase genes and the natural products potential of Dictyostelium discoideum" ''Bioinformatics'' 23:2543-49</ref>, Alveolata<ref>Zhu G, LaGier MJ, Stejskal F, Millership JJ, Cai X et al (2002) "Cryptosporidium parvum: the first protist known to encode a putative polyketide synthase" ''Gene'' 298:79-89</ref>, and animals <ref>Castoe TA, Stephens T, Noonan BP, Calestani C (2007) "A novel group of type I polyketide synthases (PKS) in animals and the complex phylogenomics of PKSs" ''Gene'' 392:47-58</ref><ref>Calestani C, Rast JP, Davidson EH (2003) "Isolation of pigment cell specific genes in the sea urchin embryo by differential macroarray screening" ''Development'' 130:4587-96</ref>. | ||
| Line 281: | Line 290: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | + | =={{Bilingual|タイプ|Type}}== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ===Type I and Type II PKS=== |
| + | |||
| + | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Type I | ||
| + | ! Type II | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | Multiple domains per protein (e.g. Erythromycin biosynthesis <ref> (2001) ''Nat Prod Rep'' 18:380</ref>) | + | Multiple domains per protein (e.g. Erythromycin biosynthesis <ref> (2001) ''Nat Prod Rep'' 18:380</ref>). The gene cluster spans at least 60 kb and synthesize macrolides and aromatic structures. |
* Bacterial type I is '''modular''', i.e., each domain (or module) catalyses a specific transformation. | * Bacterial type I is '''modular''', i.e., each domain (or module) catalyses a specific transformation. | ||
| − | * Fungal type I is '''iterative''', i.e., | + | * Fungal type I is '''iterative''', i.e., same domains are used multiple times to create large structures. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| | | | ||
| − | 複数ドメインを持つタンパク質 | + | 複数ドメインを持つタンパク質 (例.エリスロマイシン合成酵素)。 少なくとも 60 kb 以上の大きなクラスターを形成し芳香環やマクロライドのような環状化合物を作る。構造の修飾はやや限定的。 |
* バクテリアのタイプ I は、モジュール型 | * バクテリアのタイプ I は、モジュール型 | ||
* 菌類のタイプ I は反復型 | * 菌類のタイプ I は反復型 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
single domain per protein | single domain per protein | ||
| Line 312: | Line 319: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| + | |||
| + | ==={{Bilingual|タイプ III|Type III}}=== | ||
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
Chalcone synthase-like in plants | Chalcone synthase-like in plants | ||
| Line 321: | Line 330: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | ==={{Bilingual|その他|Others}}=== | |
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
;Bacterial but iterative type I PKS for aromatic polyketide | ;Bacterial but iterative type I PKS for aromatic polyketide | ||
| Line 345: | Line 354: | ||
}} | }} | ||
* NonPQU and NonJK (''Streptomyces griseus'')<ref>Kwon HJ, Smith WC, Scharon AJ, Hwang SH, Kurth MJ, Shen B (2002) C-O bond formation by polyketide synthases ''Science'' 297(5585):1327-30</ref> | * NonPQU and NonJK (''Streptomyces griseus'')<ref>Kwon HJ, Smith WC, Scharon AJ, Hwang SH, Kurth MJ, Shen B (2002) C-O bond formation by polyketide synthases ''Science'' 297(5585):1327-30</ref> | ||
| − | |||
===Unusual structures=== | ===Unusual structures=== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:24, 18 December 2012
| Polyketide Top | Species List | UniRef90 Class | UniRef50 Class | Gene Class | Domains (by CDD) |
Domains (by MAPSI) |
Polyketide
|
[edit] Overview
[edit] Structure
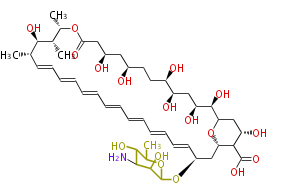
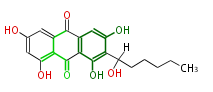
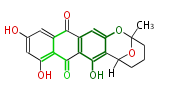
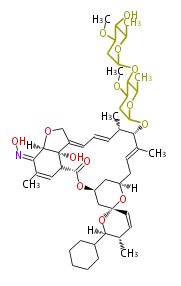
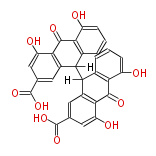
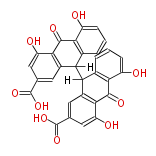
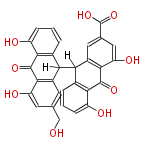
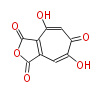
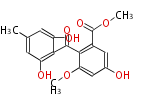
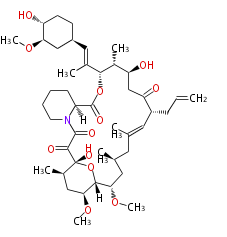
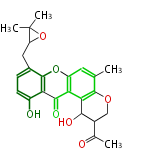
Polyketides are natural products with multiple ketone structures and synthesized from acetyl CoA. The synthetic pathway is called Acetate-Malonate Pathway. Well known products include erythromycin (antibiotic), melanin (pigment), and aflatoxin (toxin).
[edit] Acetate-Malonate Pathway
Acetyl CoA from glycolysis and its carboxylated form (malonyl CoA) are polymerized to form polyketone as in the fatty acid synthesis without reduction of carbonyl groups. Methylene moieties between ketones are highly reactive and easily Aldol- or Claisen-condensed to generate aromatic rings.
[edit] Elongation Mechanism
Polyketides are synthesized through the polymerization of acetyl units (β-ketomethylene) as in fatty acid biosynthesis. Typical starter units are short-chain fatty acids (e.g. acetyl-CoA or propionyl-CoA), on to which extender units (e.g. malonyl-CoA or methylmalonyl-CoA) are repeatedly polymerized. The key reactions for the chain extension are:
- Claisen condensation by β-ketoacyl synthase (KS)
- an acyltransferase (AT), and
- an acyl carrier protein (ACP).
After elongation, β-ketone is reduced. In fatty acid biosynthesis, the chain is fully reduced by the following three steps:
- Reduction to an alcohol by ketoreductase (KR),
- Dehydration to the conjugated ester by dehydratase (DH), and
- Reduction of the double bond by enoyl reductase (ER).
Finally, the chain is terminated by a thioesterase (TE) activity and allows Claisen cyclization (CYC).
[edit] Polyketide Synthase (PKS)
[edit] Distribution
PKS members are found in bacteria, fungi, plants, slime mold[1], Alveolata[2], and animals [3][4].
| Species | Actinomycetes | Cyanobacteria | γ-Proteobacteria | Fungi | Alveolata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type-I PKS | Ο | Ο | Ο | Ο | Ο |
| Type-II PKS | Ο | Χ | Χ | Χ | Χ |
| NRPS | Ο | Ο | Ο | Ο | Χ |
| deoxysugar | Ο | Χ | Χ | Χ | Χ |
| Terpene | Δ | Χ | Χ | Ο | Χ |
- References
- ↑ Zucko J, Skunca N, Curk T, Zupan B, Long PF et al (2007) "Polyketide synthase genes and the natural products potential of Dictyostelium discoideum" Bioinformatics 23:2543-49
- ↑ Zhu G, LaGier MJ, Stejskal F, Millership JJ, Cai X et al (2002) "Cryptosporidium parvum: the first protist known to encode a putative polyketide synthase" Gene 298:79-89
- ↑ Castoe TA, Stephens T, Noonan BP, Calestani C (2007) "A novel group of type I polyketide synthases (PKS) in animals and the complex phylogenomics of PKSs" Gene 392:47-58
- ↑ Calestani C, Rast JP, Davidson EH (2003) "Isolation of pigment cell specific genes in the sea urchin embryo by differential macroarray screening" Development 130:4587-96
[edit] Type
[edit] Type I and Type II PKS
| Type I | Type II |
|---|---|
|
Multiple domains per protein (e.g. Erythromycin biosynthesis [1]). The gene cluster spans at least 60 kb and synthesize macrolides and aromatic structures.
|
single domain per protein
|
[edit] Type III
Chalcone synthase-like in plants
- Discovered in plants, but later found in bacteria[2]
[edit] Others
- Bacterial but iterative type I PKS for aromatic polyketide
- AviM for orsellinic acid biosynthesis (Streptomyces viridochromogens Tu57)[3]
- CalO5 for calicheamicin biosyntehsis (Micromonospora echinospora ssp. calichenisis)[4]
- NesB for neocarzinostatin biosynthesis (?)[5]
- Type I PKS that lacks the cognate AT domain
- lnmIJ for leinamycin biosynthesis (Streptomyces atroolivaceus S-140)[6]
- PedF for pederin biosynthesis (symbiont bacterium of Paederus beetles)[7]
- Type II PKS that act non-iteratively and use acyl CoA as substrates directly
- NonPQU and NonJK (Streptomyces griseus)[8]
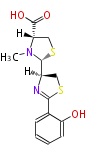
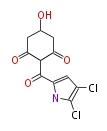
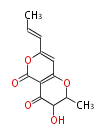
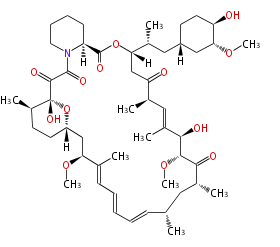
[edit] Unusual structures
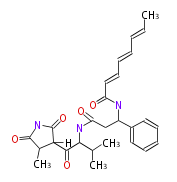
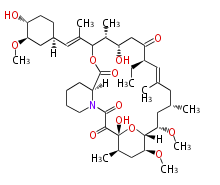
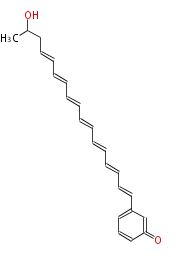
| Phoma | zaragozic acid, phomoidoride | Streptomyces | yatakemycin, leinamycin, saframycin, neocarzinostatin, staurosporin, FR182877 | Other bacteria | PKS-NRPS hybrid type
Curacin A (Lyngbya), Shiphonazole (Herpetosiphon), Jamaicamide A (Lyngbya), Cylindrospermopsin (Cylindrospermopsis) |
|---|
[edit] Non-ribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS)
Coupling with PKS and NRPS
- vancomycin ()
- leinamycin (Curr opin chem biol 7:285, 2003)
- pseurotin (chem bio chem 8:1736-1743, 2007)
- curacin (curr opin chem biol 13:216, 2009)
- epothilone
- rapamycin
[edit] Decoration
deoxysugars
deoxygenation, c-methylation, amination, n-methylation, ketosugar,
- References
- ↑ (2001) Nat Prod Rep 18:380
- ↑ Moore BS, Hopke JN (2001) Discovery of a new bacterial polyketide biosynthetic pathway Chembiochem 2:35-8
- ↑ Gaisser S, Trefzer A, Stockert S, Kirschning A, Bechthold A (1997) Cloning of an avilamycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tu57. J Bacteriol 179:6271-8
- ↑ Whitwam RE, Ahlert J, Holman TR, Ruppen M, Thorson JS (2000) The gene calC encodes for a non-heme iron metalloprotein responsible for calicheamicin self-resistance in Micromonospora. J Am Chem Soc 122:1556-7
- ↑ Zazopoulos E, Huang K, Staffa A, Liu W, Bachmann BO, Nonaka K, Ahlert J, Thorson JS, Shen B, Farnet CM (2003) A genomics-guided approach for discovering and expressing cryptic metabolicpathways Nat Biotechnol epub.
- ↑ Cheng Y-Q, Tang G-L, Shen B (2003) Type I polyketide synthase requiring a discrete acyltransferase for polyketide biosynthesis Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: in press
- ↑ Piel J (2002) A polyketide synthase-peptide synthetase gene cluster from an uncultured bacterial symbiont of Paederus beetles Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:14808-13
- ↑ Kwon HJ, Smith WC, Scharon AJ, Hwang SH, Kurth MJ, Shen B (2002) C-O bond formation by polyketide synthases Science 297(5585):1327-30