Category:BMAA
Amino Acids
| Basic Metabolism Top (代謝トップ) |
Molecule Index (化合物索引) |
EC classes ( EC分類) |
Input New Data (新規入力) |
Upper classes : BM Basic Metabolites
Contents |
Class Overview
<p> An amino acid has a carbon connected by an amino group and a carboxyl group (called an alpha carbon). Proteins are constituted from 20 amino acids.
</p>| Straight Class | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMAAS2 (1 pages) | Straight length 2 Gly 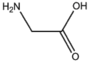
|
BMAAS3 (19 pages) | Straight length 3 Ser, Cys, Ala 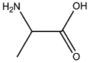
|
BMAAS4 (16 pages) | Straight length 4 Asp, Asn, Thr 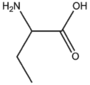
|
| BMAAS5 (16 pages) | Straight length 5 Gln, Glu 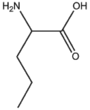
|
BMAAS6 (6 pages) | Straight length 6 Lys 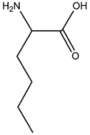
|
||
| Branched Class | |||||
| BMAAB4 (2 pages) | Branched length 4 Val, Met 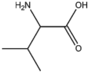
|
BMAAB5 (3 pages) | Branched length 5 Arg, Leu, Ile 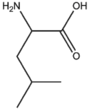
|
BMAAB6 (0 pages) | Branched length 6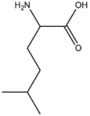
|
| Cyclic Class (click here to visit another page) | |||||
Physicochemical Characters
| Character of amino acids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Code | Symbol | Structure | Character | pI | Required for human? |
| BMAAS3AK0003 | Ala | A | -CH3 | neutral | 6.0 | |
| BMAAS3HO0002 | Ser | S | -CH2OH | neutral | 5.7 | |
| BMAAS4HO0004 | Thr | T | -CH(OH)CH3 | neutral | 5.6 | yes |
| BMAAB4AK0001 | Val | V | -CH(CH3)2 | neutral, branched | 6.0 | yes |
| BMAAB5AK0003 | Leu | L | -CH2CH(CH3)2 | neutral, branched | 6.0 | yes |
| BMAAB5AK0002 | Ile | I | -CH(CH3)CH2CH3 | neutral, branched | 6.0 | yes |
| BMAAS4AL0001 | Asp | D | -CH2COOH | acidic | 2.8 | |
| BMAAS5AL0002 | Glu | E | -CH2CH2COOH | acidic | 3.2 | |
| BMAAS4AM0002 | Asn | N | -CH2CONH2 | acidic, amido | 5.4 | |
| BMAAS5AM0002 | Gln | Q | -CH2CH2CONH2 | acidic, amido | 5.7 | |
| BMAAS6AN0005 | Lys | K | -(CH2)4NH3 | basic | 9.7 | yes |
| BMAAS5AN0003 | Arg | R | -(CH2)3NHC(=NH)NH2 | basic | 10.8 | |
| BMAAS3SF0003 | Cys | C | -CH2SH | neutral, S | 5.1 | |
| BMAAS4SF0003 | Met | M | -(CH2)2SCH3 | neutral, S | 5.7 | yes |
| BMACBZ--0005 | Phe | F | -CH2-Benz | neutral, aromatic | 5.5 | yes |
| BMACBZHO0008 | Tyr | Y | -CH2-Benz-OH | neutral, aromatic | 5.7 | |
| BMACID--0003 | Trp | W | -CH2-Indole | neutral, aromatic | 5.9 | yes |
| BMACIZ--0002 | His | H | -CH2-Imidazole | basic, atomatic | 7.6 | yes |
| BMACPL--0008 | Pro | P | -NH-(CH2)3- | neutral, cyclic, 2nd amine | 6.2 | |
D and L in Amino Acid
Definition
Except for glycine, an amino acid contains a chiral carbon, distinguished by D or L (R or S). In the Fischer projection, which places the carboxyl group upward and amino acid-specific side-chain downward, the amino group must comes either left or right, protruding from the paper plane. If the hydrogen is left and amino group is right, the amino acid is called D, after D-glyceraldehide. If the amino group is left, it is called L.
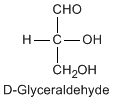
|
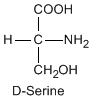
|
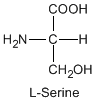
|
DL and RS do not coincide
In the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (or RS) notation, 19 L-amino acids become S-form (when H is placed behind the paper plane, the amino group, carboxyl group and side chain are arranged anticlockwise). Only L-cysteine becomes R-form because S in its side chain makes the arrangement in the different order: amino group, side chain, and carboxyl group. For this reason, although its tetrahedal configuration is the same as the rest of amino acids, it is R-form. Likewise, cystine is R-form too.
Glycine has no chiral carbon
Glycine has two Hydrogen branches and therefore not chiral. The amino group of proline is included in the ring sturucture and therefore secondary amine.
This category currently contains no pages or media.