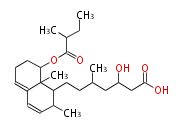Category:PK
m |
m |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* an acyltransferase ('''AT'''), and | * an acyltransferase ('''AT'''), and | ||
* an acyl carrier protein ('''ACP'''). | * an acyl carrier protein ('''ACP'''). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | + | ポリケチドは脂肪酸の合成に同じく、アセチル単位 (β-ケトメチレン鎖) の重合によって作られます。よく使われる初期ユニットはアセチルCoAやプロピオニルCoAで、それらをマロニルCoAやメチルマロニルCoAで伸張していきます。 | |
鎖の伸長に使う反応は | 鎖の伸長に使う反応は | ||
* β-ケトアシル合成酵素 ('''KS''') によるクライゼン縮合 | * β-ケトアシル合成酵素 ('''KS''') によるクライゼン縮合 | ||
| Line 28: | Line 19: | ||
* アシル輸送タンパク質 ('''ACP''') | * アシル輸送タンパク質 ('''ACP''') | ||
です。 | です。 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | {{Twocolumn| | |
| + | After elongation, β-ketone is reduced. In fatty acid biosynthesis, the chain is fully reduced by the following three steps: | ||
| + | * Reduction to an alcohol by ketoreductase ('''KR'''), | ||
| + | * Dehydration to the conjugated ester by dehydratase ('''DH'''), and | ||
| + | * Reduction of the double bond by enoyl reductase ('''ER'''). | ||
| + | In polyketide synthase, the reduction is patial. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | 伸張の後に、ケト基を還元します。完全に還元して酸素を除くと脂肪酸になりますが、ポリケチドの多くは還元が部分的にストップします。重要な反応は | ||
* ケト還元酵素 ('''KR''') によるアルコールへの還元 | * ケト還元酵素 ('''KR''') によるアルコールへの還元 | ||
* 脱水酵素 ('''DH''') による共役エステルからの脱水 | * 脱水酵素 ('''DH''') による共役エステルからの脱水 | ||
* エノイル還元酵素 ('''ER''') による二重結合の還元 | * エノイル還元酵素 ('''ER''') による二重結合の還元 | ||
です。 | です。 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| + | Finally, the chain is terminated by a thioesterase ('''TE''') activity and | ||
| + | allows Claisen cyclization ('''CYC'''). | ||
| + | | | ||
最後に、チオエステル分解酵素 ('''TE''') によって伸張が止まり、ラクトン化 (閉環) します。 | 最後に、チオエステル分解酵素 ('''TE''') によって伸張が止まり、ラクトン化 (閉環) します。 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | !colspan=" | + | !colspan="3" style="background:lightgray"| Linear Chain and Related (L) |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Straight (LS) | ! Straight (LS) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 84: | Line 88: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Polyether (LE) | ! Polyether (LE) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 102: | Line 106: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan=" | + | !colspan="3" style="background:lightgray"| Aromatic and Diels-Alder Related (most often by iterative type II) |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Monocyclic (A1) | ! Monocyclic (A1) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 117: | Line 121: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Bicyclic (A2) | ! Bicyclic (A2) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 125: | Line 129: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Tricyclic (A3) | ! Tricyclic (A3) | ||
|- | |- | ||
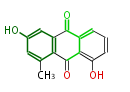
| Line 134: | Line 138: | ||
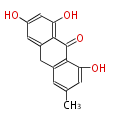
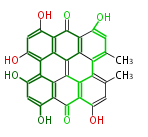
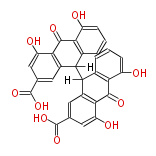
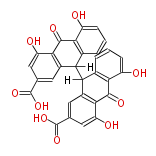
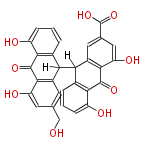
| hypericin | | hypericin | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! Tetracyclic (A4) | ! Tetracyclic (A4) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 142: | Line 147: | ||
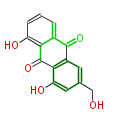
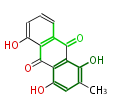
| Angucycline | | Angucycline | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" | ||
| + | ! Others (AO) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | ? | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !colspan="3" style="background:lightgray"| Macrolides (most often by non-iterative type I) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: | + | |style="width:200px"| |
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! 12-membered (M2) | ! 12-membered (M2) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |style="width: | + | |style="width:200px"| |
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! 14-membered (M4) | ! 14-membered (M4) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 196: | Line 174: | ||
| Zearalenone | | Zearalenone | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |style="width: | + | |style="width:200px"| |
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
! 16-membered (M6) | ! 16-membered (M6) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 208: | Line 186: | ||
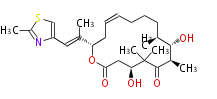
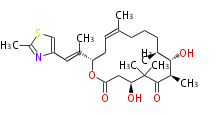
| Tylosin | | Tylosin | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |style="width: | + | |- |
| − | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width: | + | |style="width:200px"| |
| − | ! | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" |
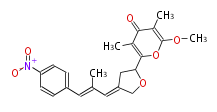
| + | ! Polyene (MN) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Manumycin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Nystatin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Amphotericin | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |style="width:200px"| | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" | ||
| + | ! Polyether (ME) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Nonactin, Nactin | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |style="width:200px"| | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" | ||
| + | ! Cyclic Imines (MI) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Spirolide | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Pinnatoxin | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:200px"| | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" | ||
| + | ! Ansamacrolide (MA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Rifamycin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Ansamycin | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |style="width:200px"| | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" style="width:200px" | ||
| + | ! Others (MO) | ||
|- | |- | ||
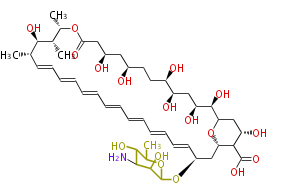
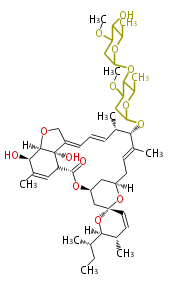
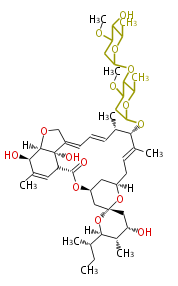
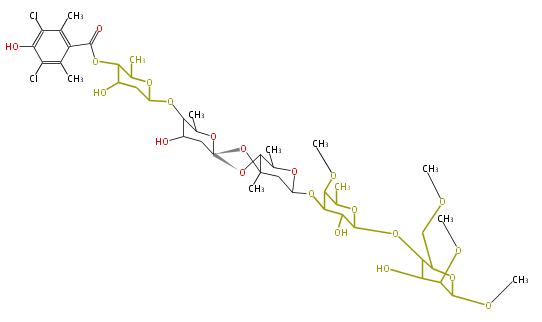
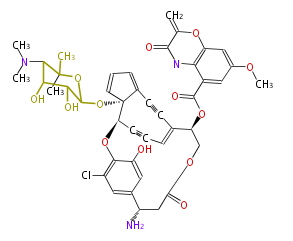
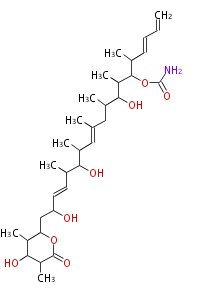
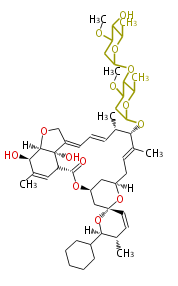
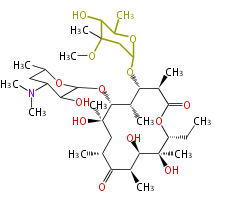
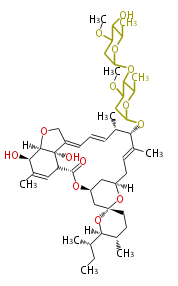
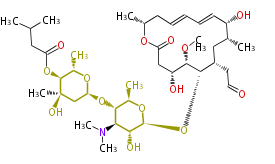
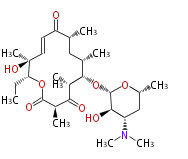
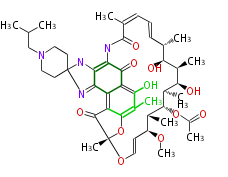
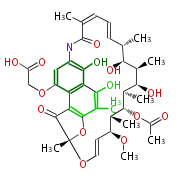
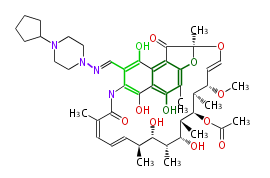
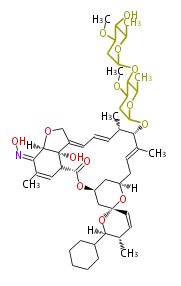
| Bryostatin (26)<ref>It lacks AT domain as in mupirocin, leinamycin<ref>Nguyen T, Ishida K, Jenke-Kodama H, Dittmann E, Gurgui C, Hochmuth T, Taudien S, Platzer M, Hertweck C, Piel J (2008) "Exploiting the mosaic structure of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases for natural product discovery and pathway dissection" ''Nat Biotechnol'' 26:225 - 233 PMID 18223641</ref> | | Bryostatin (26)<ref>It lacks AT domain as in mupirocin, leinamycin<ref>Nguyen T, Ishida K, Jenke-Kodama H, Dittmann E, Gurgui C, Hochmuth T, Taudien S, Platzer M, Hertweck C, Piel J (2008) "Exploiting the mosaic structure of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases for natural product discovery and pathway dissection" ''Nat Biotechnol'' 26:225 - 233 PMID 18223641</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 18 December 2010
Polyketide (ポリケチド)
|
Class Overview
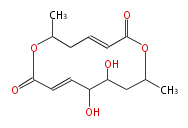
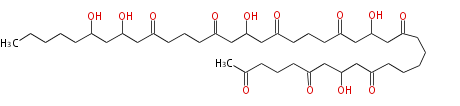
Polyketides are synthesized through the polymerization of acetyl units (β-ketomethylene) as in fatty acid biosynthesis. Typical starter units are short-chain fatty acids (e.g. acetyl-CoA or propionyl-CoA), on to which extender units (e.g. malonyl-CoA or methylmalonyl-CoA) are repeatedly polymerized. The key reactions for the chain extension are:
- Claisen condensation by β-ketoacyl synthase (KS)
- an acyltransferase (AT), and
- an acyl carrier protein (ACP).
After elongation, β-ketone is reduced. In fatty acid biosynthesis, the chain is fully reduced by the following three steps:
- Reduction to an alcohol by ketoreductase (KR),
- Dehydration to the conjugated ester by dehydratase (DH), and
- Reduction of the double bond by enoyl reductase (ER).
Finally, the chain is terminated by a thioesterase (TE) activity and allows Claisen cyclization (CYC).
| 1st Class | ||
|---|---|---|
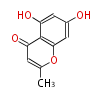
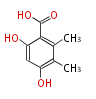
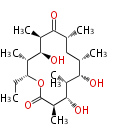
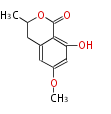
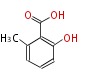
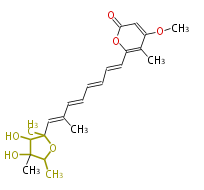
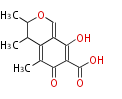
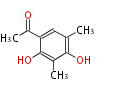
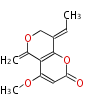
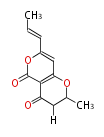
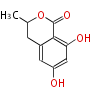
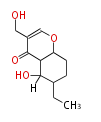
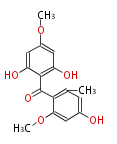
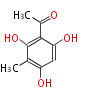
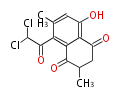
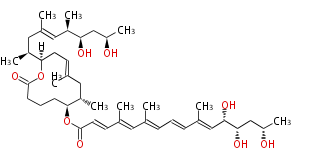
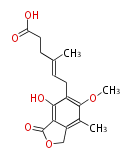
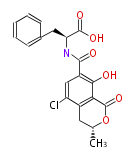
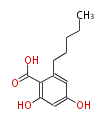
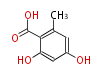
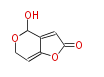
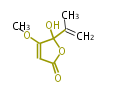
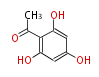
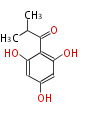
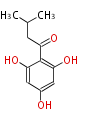
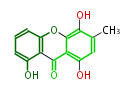
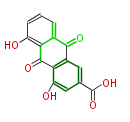
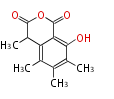
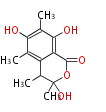
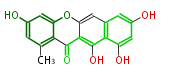
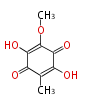
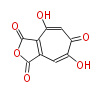
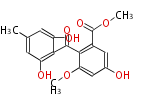
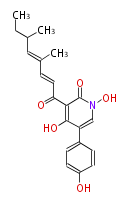
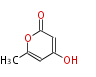
| PK4: Four C2 Units orsellinic acid, 6-methylsalicylic acid, triacetic acid lactone, asperlin, usnic acid, methylphloracetophenone, penicillic acid, patulin |
PK5: Five C2 Units citrinin, aflatoxin, augenone, sepedonin, stipitatonic acid |
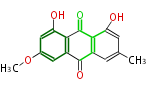
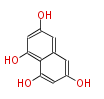
PK6: Six C2 Units plumbagin, 7-methyljuglone, juglone, variotin |
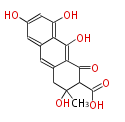
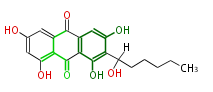
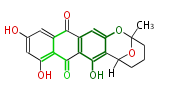
| PK7: Seven and eight C2 Units Anthraquinone rings |
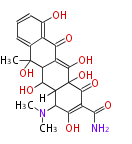
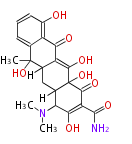
PK9: Nine C2 Units Tetracyclines | |
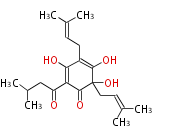
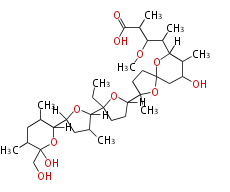
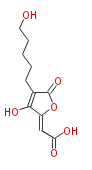
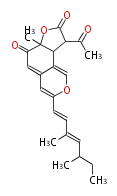
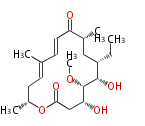
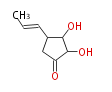
| Linear Chain and Related (L) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
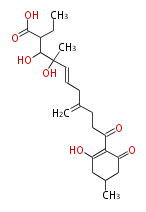
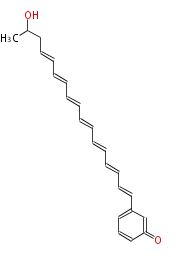
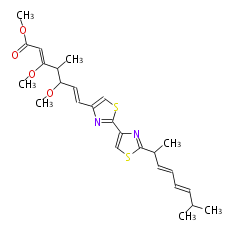
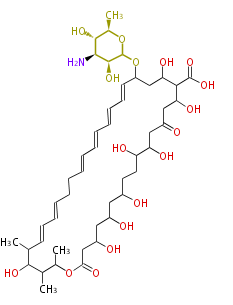
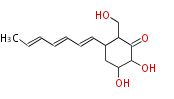
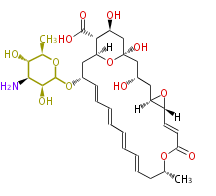
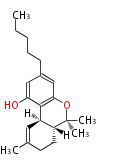
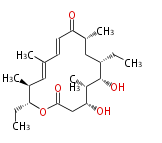
Acetogenins (LA) | ||||||||||||
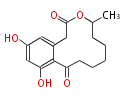
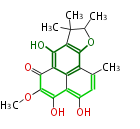
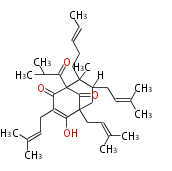
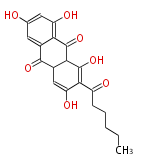
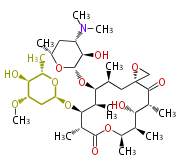
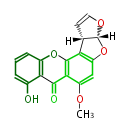
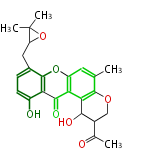
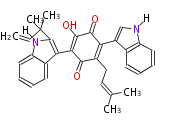
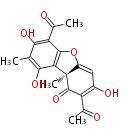
| Aromatic and Diels-Alder Related (most often by iterative type II) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
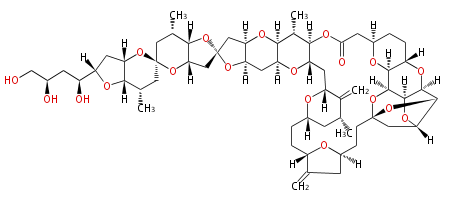
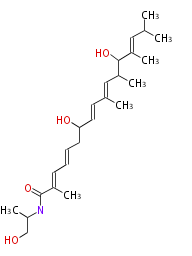
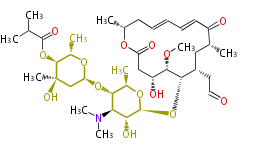
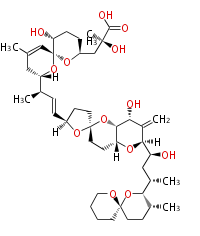
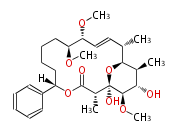
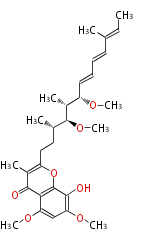
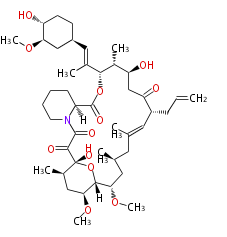
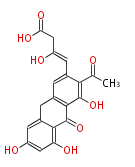
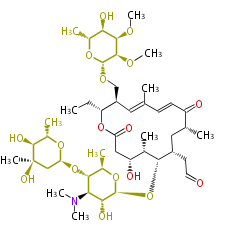
| Macrolides (most often by non-iterative type I) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
Polyketide Synthase (PKS)
| species | Actinomycetes | Cyanobacteria | γ-Proteobacteria | Fungi | Dinoflagellates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type-I PKS | Ο | Ο | Ο | Χ | Ο |
| Type-II PKS | Ο | Χ | Χ | Ο | Χ |
| NRPS | Ο | Ο | Ο | Ο | Χ |
| deoxysugar | Ο | Χ | Χ | Χ | Χ |
| Terpene | Δ | Χ | Χ | Ο | Χ |
Type I PKS (non-iterative)
- Multi catalytic domains exist in a single protein
- Chain length is determined by the number of catalytic domains.
- Products are non-aromatic and have larger masses.
Ref. Erythromycin biosynthesis in Nat Prod Rep 18, 380 (2001)
Type II PKS (iterative)
- Three proteins (KSα, KSβ, ACP) are repeatedly used for carbon chain elongation.
- Chain length is determined by another protein, CLF.
- In bacteria, products are aromatic (e.g. chiorotetracycline, pradimicin).
- In fungi, products are both non-aromatic and aromatic.
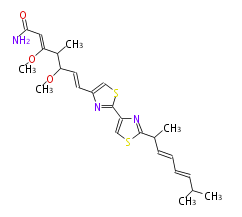
Non-ribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS)
Coupling with PKS and NRPS
- vancomycin ()
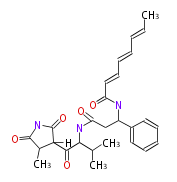
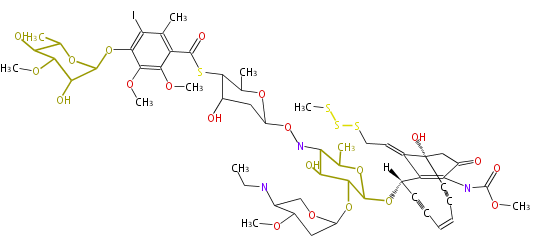
- leinamycin (Curr opin chem biol 7:285, 2003)
- pseurotin (chem bio chem 8:1736-1743, 2007)
- curacin (curr opin chem biol 13:216, 2009)
- epothilone
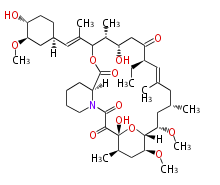
- rapamycin
PKS in Fungi
- both aromatic and non-aromatic compounds are generated by iterative PKS
- methyl branch is transferred from methionine, not methylmalonyl CoA
Ref. Dewick, PM Medicinal Natural Products (2009)
Decoration
deoxysugars
deoxygenation, c-methylation, amination, n-methylation, ketosugar,
Unusual structures
| Phoma | zaragozic acid, phomoidoride | Streptomyces | yatakemycin, leinamycin, saframycin, neocarzinostatin, staurosporin, FR182877 | Other bacteria | PKS-NRPS hybrid type
Curacin A (Lyngbya), Shiphonazole (Herpetosiphon), Jamaicamide A (Lyngbya), Cylindrospermopsin (Cylindrospermopsis) |
|---|
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found