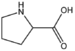Category:BM
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
<!--- Class Information (Do not delete. It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) | <!--- Class Information (Do not delete. It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) | ||
&&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | &&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | ||
| − | &&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | + | &&BMIO&&Inorganics 無機物&& |
&&BMIOOX&&oxidized elements 酸化物(no C)&& | &&BMIOOX&&oxidized elements 酸化物(no C)&& | ||
&&BMIOMT&&metals and halogens 金属、ハロゲン&& | &&BMIOMT&&metals and halogens 金属、ハロゲン&& | ||
| Line 174: | Line 174: | ||
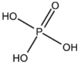
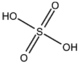
&&BMIOSF&&sulfates 硫黄&& | &&BMIOSF&&sulfates 硫黄&& | ||
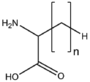
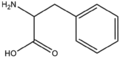
| − | &&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | + | &&BMAA&&Amino acids アミノ酸&& |
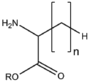
&&BMAAS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMAAS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
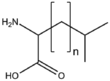
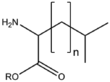
&&BMAAB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMAAB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| − | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives&& | + | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives アミノ酸誘導体&& |
&&BMAXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMAXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMAXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMAXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
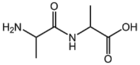
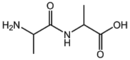
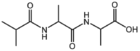
| − | &&BMAXDP&&di-peptide&& | + | &&BMAXDP&&di-peptide ジペプチド&& |
| − | &&BMAXTP&&tri-peptide&& | + | &&BMAXTP&&tri-peptide トリペプチド&& |
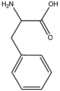
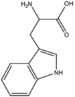
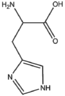
| − | &&BMAC&&Cyclic amino acids&& | + | &&BMAC&&Cyclic amino acids 環状アミノ酸&& |
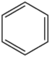
| − | &&BMACBZ&&benzene ring&& | + | &&BMACBZ&&benzene ring ベンゼン&& |
| − | &&BMACID&&indole ring&& | + | &&BMACID&&indole ring インドール&& |
| − | &&BMACPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | + | &&BMACPL&&pyrrolidine ring ピロリジン&& |
| − | &&BMACIZ&&imidazole ring&& | + | &&BMACIZ&&imidazole ring イミダゾール&& |
| − | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | + | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl 脂肪酸&& |
&&BMFYS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMFYS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMFYB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMFYB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| − | &&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle&& | + | &&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle 単、複合環&& |
| − | &&BMMCBZ&&benzene ring&& | + | &&BMMCBZ&&benzene ring ベンゼン環&& |
&&BMMCBZ1S&&0-1 substitution&& | &&BMMCBZ1S&&0-1 substitution&& | ||
&&BMMCBZ2O&&2 substitutions (ortho)&& | &&BMMCBZ2O&&2 substitutions (ortho)&& | ||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
&&BMMCBZ4S&&with 4-6 substitutions&& | &&BMMCBZ4S&&with 4-6 substitutions&& | ||
| − | &&BMMCPY&&pyrimidine | + | &&BMMCPY&&pyrimidine ring ピリミジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYCT&&cytosine&& | + | &&BMMCPYCT&&cytosine シトシン&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYTY&&thymine&& | + | &&BMMCPYTY&&thymine チミン&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYUR&&uracil&& | + | &&BMMCPYUR&&uracil ウラシル&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYXX&&others&& | + | &&BMMCPYXX&&others その他&& |
| − | &&BMMCPD&&pyridine ring&& | + | &&BMMCPD&&pyridine ring ピリジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCIZ&&imidazole ring&& | + | &&BMMCIZ&&imidazole ring イミダゾール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCTZ&&thiazole ring&& | + | &&BMMCTZ&&thiazole ring チアゾール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCQN&&quinone ring&& | + | &&BMMCQN&&quinone ring キノン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCVA&&retinol ring&& | + | &&BMMCVA&&retinol ring レチノール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | + | &&BMMCPL&&pyrrolidine ring ピロリジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCLA&&lacton&& | + | &&BMMCLA&&lacton ラクトン&& |
| − | &&BMMCAC&&aliphatic cycle&& | + | &&BMMCAC&&aliphatic cycle 脂肪族環&& |
| − | &&BMMCACCH&&cyclohexane&& | + | &&BMMCACCH&&cyclohexane シクロヘキサン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACEN&&cyclohexene&& | + | &&BMMCACEN&&cyclohexene シクロヘキセン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACDE&&cyclohexadiene&& | + | &&BMMCACDE&&cyclohexadiene シクロヘキサジエン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACXX&&others&& | + | &&BMMCACXX&&others その他&& |
| − | &&BMMCHC&&hetero cyclic&& | + | &&BMMCHC&&hetero cyclic ヘテロ環&& |
| − | &&BMMCAS&&assembled&& | + | &&BMMCAS&&assembled 複合環&& |
| − | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle&& | + | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle 共役環&& |
| − | &&BMCCPU&&purine ring&& | + | &&BMCCPU&&purine ring プリン環&& |
&&BMCCPUAD&&アデニン(アデニン、ヌクレオシド)&& | &&BMCCPUAD&&アデニン(アデニン、ヌクレオシド)&& | ||
&&BMCCPUAP&&アデニン(ヌクレオチド)&& | &&BMCCPUAP&&アデニン(ヌクレオチド)&& | ||
| Line 250: | Line 250: | ||
&&BMCCBR&&bridged structure 架橋環構造&& | &&BMCCBR&&bridged structure 架橋環構造&& | ||
| − | &&BMXX&&Others&& | + | &&BMXX&&Others その他&& |
&&BMXXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMXXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMXXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMXXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
Revision as of 04:13, 6 September 2008
Basic Metabolites (基礎代謝物)
Class Overview
(The following description is translated from an article by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.)
Metabolism is the total body of physicochemical reactions inside living systems. It can be functionally divided into two groups: the basic (or primary) metabolism essential for maintenance of life systems, and the non-essential secondary metabolism. Basic metabolites therefore include bases, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids (building blocks of DNA, protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively). Also included are lignin and cellulose which are essential for plant growth. On the other hand, the secondary metabolism provides species-specific functions. It includes medicinal metabolites such as antibiotics and herbal medicines.
Biosynthesis 生合成
Subcategories
This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.