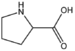Category:BM
m (→{{Bilingual|Metabolite Category|代謝物の種類}}) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Huge|Basic | + | {{Huge|Basic Metabolism (基礎代謝)}} |
| − | + | {{Basic Metabolism/Header}} | |
| − | ==Class Overview== | + | =={{Bilingual|概要|Class Overview}}== |
{{Twocolumn| | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| − | (The following description is translated from an article by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.) | + | (The following description is translated from an article written by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.) |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | Metabolism is the total body of physicochemical reactions inside living systems. It can be functionally divided into two groups: the basic (or primary) metabolism essential for maintenance of life systems, and the non-essential secondary metabolism. Basic metabolites therefore include bases, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids (building blocks of DNA, protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively). Also included are lignin and cellulose which are essential for plant growth. On the other hand, the secondary metabolism provides species-specific functions. It includes medicinal metabolites such as antibiotics and | + | Metabolism is the total body of physicochemical reactions inside living systems. It can be functionally divided into two groups: the basic (or primary) metabolism essential for maintenance of life systems, and the non-essential secondary metabolism. Basic metabolites therefore include bases, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids (building blocks of DNA, protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively). Also included are lignin and cellulose which are essential for plant growth. On the other hand, the secondary metabolism provides species-specific functions. It includes medicinal metabolites such as antibiotics and crude drugs. |
| | | | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
代謝とは, 生体内でおこなわれる物理化学反応の総体, または特定の分子に関与する物理化学反応の総体です. 機能の観点から, 生命の維持に必須の物質群に関わる基礎/一次代謝と, 生命維持に必須ではない二次代謝に分けられます. 生命に欠かせない核酸, アミノ酸, 糖, 脂肪酸 (それぞれDNA,タンパク質,炭水化物, 脂質の構成単位) は基礎代謝物とよばれ, また植物に必須のリグニンやセルロースも基礎代謝物に分類されます. これに対し二次代謝は, 生物種に固有の機能を提供する部分です. 抗生物質や生薬など, 人間が利用してきた薬効成分はいずれも二次代謝物に属します. | 代謝とは, 生体内でおこなわれる物理化学反応の総体, または特定の分子に関与する物理化学反応の総体です. 機能の観点から, 生命の維持に必須の物質群に関わる基礎/一次代謝と, 生命維持に必須ではない二次代謝に分けられます. 生命に欠かせない核酸, アミノ酸, 糖, 脂肪酸 (それぞれDNA,タンパク質,炭水化物, 脂質の構成単位) は基礎代謝物とよばれ, また植物に必須のリグニンやセルロースも基礎代謝物に分類されます. これに対し二次代謝は, 生物種に固有の機能を提供する部分です. 抗生物質や生薬など, 人間が利用してきた薬効成分はいずれも二次代謝物に属します. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =={{Bilingual|Metabolite Category|代謝物の種類}}== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Aritalab:Lecture/Biochem/Amino Acid|アミノ酸]] | ||
| + | * [[Aritalab:Lecture/Biochem/Saccharide|糖]] | ||
| + | * [[Aritalab:Lecture/Biochem/Nucleic Acid|核酸]] | ||
| + | * [[Aritalab:Lecture/Biochem/Lipid|脂質]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Design of Basic Metabolite ID numbers <small>ID番号の設計</small>== | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | 12-DIGIT | ||
| + | <table border=1> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:yellowgreen;" width=15px align="center"><big>B</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:yellowgreen;" width=15px align="center"><big>M</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:darkseagreen;" width=15px align="center"><big>''a''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:darkseagreen;" width=15px align="center"><big>''a''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:tomato; color:white" width=15px align="center"><big>''b''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:tomato; color:white" width=15px align="center"><big>''b''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:firebrick; color:white" width=15px align="center"><big>''c''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:firebrick; color:white" width=15px align="center"><big>''c''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:green; color:white;" width=15px align="center"><big>''d''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:green; color:white" width=15px align="center"><big>''d''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:white;" width=15px align="center"><big>''e''</big> | ||
| + | <td style="background-color:white;" width=15px align="center"><big>''e''</big> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | {{Twocolumn| | ||
| + | * ''a'' ... Structure type (Table 1) | ||
| + | * ''b'' ... degree of unsaturation (Table 2) | ||
| + | * ''c'' ... position of n-''z'' (n minus z; also ω-z or omega-z) nomenclature (Table 3) | ||
| + | * ''d'' ... structure type (Table 4) | ||
| + | * ''e'' ... serial number | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * ''a'' ... 炭素鎖長(Table 1) | ||
| + | * ''b'' ... 不飽和度(Table 2) | ||
| + | * ''c'' ... n-''z'' (またはω-''z''やomega-''z'') における数(Table 3) | ||
| + | * ''d'' ... 骨格のタイプ (Table 4) | ||
| + | * ''e'' ... 通し番号 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 45: | Line 86: | ||
! colspan="2"|2nd Class | ! colspan="2"|2nd Class | ||
|- | |- | ||
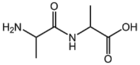
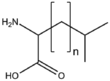
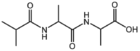
| − | |[[:Category:BMAA|BMAASn]]||[[:Category:BMAA|Straight chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAASn.png| | + | |[[:Category:BMAA|BMAASn]]||[[:Category:BMAA|Straight chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAASn.png|90px]] |
|- | |- | ||
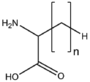
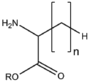
| − | |[[:Category:BMAA|BMAABn]]||[[:Category:BMAA|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAABn.png| | + | |[[:Category:BMAA|BMAABn]]||[[:Category:BMAA|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAABn.png|110px]] |
|} | |} | ||
|align="center" valign="center"| | |align="center" valign="center"| | ||
| Line 56: | Line 97: | ||
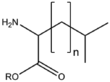
|[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXSn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Straight chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXSn.png|90px]] | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXSn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Straight chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXSn.png|90px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXBn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXBn.png| | + | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXBn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXBn.png|110px]] |
|- | |- | ||
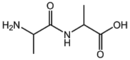
| − | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXDP]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Dipeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXDP.png| | + | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXDP]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Dipeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXDP.png|130px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXTP]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Tripeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXTP.png| | + | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXTP]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Tripeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXTP.png|140px]] |
|} | |} | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| Line 139: | Line 180: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMFY|BMFY: | + | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMFY|BMFY: Fat acyl]]<br>アシル<br>[[Image:BMFY.png|100px]]<br>Tree-shaped<br>樹状のもの |
| + | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMSU|BMSU: Sugar]]<br>炭水化物<br>[[Image:BMSU.png|100px]]<br>mono, disaccharide<br>単糖、二糖 | ||
|align="center"|[[:Category:BMXX|BMXX: Others]]<br>その他<br> [[Image:BMXX.png|100px]] | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMXX|BMXX: Others]]<br>その他<br> [[Image:BMXX.png|100px]] | ||
| − | |||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|align="center" valign="center"| | |align="center" valign="center"| | ||
| Line 151: | Line 192: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[:Category:BMFY|BMFYBn]]||[[:Category:BMFY|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMFYBn.png|80px]] | |[[:Category:BMFY|BMFYBn]]||[[:Category:BMFY|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMFYBn.png|80px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |align="center" valign="center"| | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed" border="1" cellspacing="0" width="150" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="2"|2nd Class | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[:Category:BMSU|BMSUM4]]||[[:Category:BMSU|Monosaccharide (C4)]]<br>[[Image:BMSUM4.png|70px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[:Category:BMSU|BMSUM5]]||[[:Category:BMSU|Monosaccharide (C5)]]<br>[[Image:BMSUM5.png|70px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[:Category:BMSU|BMSUM6]]||[[:Category:BMSU|Monosaccharide (C6)]]<br>[[Image:BMSUM6.png|70px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[:Category:BMSU|BMSUM7]]||[[:Category:BMSU|Monosaccharide (C >7 )]]<br>[[Image:BMSUM7.png|70px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
|align="center" valign="center"| | |align="center" valign="center"| | ||
| Line 161: | Line 215: | ||
|[[:Category:BMXX|BMXXBx]]||[[:Category:BMXX|Branched]]<br>[[Image:BMXXBX.png|60px]] | |[[:Category:BMXX|BMXXBx]]||[[:Category:BMXX|Branched]]<br>[[Image:BMXXBX.png|60px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 167: | Line 220: | ||
<!--- Class Information (Do not delete. It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) | <!--- Class Information (Do not delete. It is used by Template:Hierarchy.) | ||
&&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | &&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | ||
| − | &&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | + | &&BMIO&&Inorganics 無機物&& |
&&BMIOOX&&oxidized elements 酸化物(no C)&& | &&BMIOOX&&oxidized elements 酸化物(no C)&& | ||
&&BMIOMT&&metals and halogens 金属、ハロゲン&& | &&BMIOMT&&metals and halogens 金属、ハロゲン&& | ||
| Line 174: | Line 227: | ||
&&BMIOSF&&sulfates 硫黄&& | &&BMIOSF&&sulfates 硫黄&& | ||
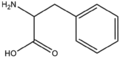
| − | &&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | + | &&BMAA&&Amino acids アミノ酸&& |
&&BMAAS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMAAS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMAAB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMAAB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| − | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives&& | + | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives アミノ酸誘導体&& |
&&BMAXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMAXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMAXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMAXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| − | &&BMAXDP&&di-peptide&& | + | &&BMAXDP&&di-peptide ジペプチド&& |
| − | &&BMAXTP&&tri-peptide&& | + | &&BMAXTP&&tri-peptide トリペプチド&& |
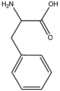
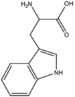
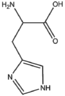
| − | &&BMAC&&Cyclic amino acids&& | + | &&BMAC&&Cyclic amino acids 環状アミノ酸&& |
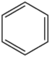
| − | &&BMACBZ&&benzene ring&& | + | &&BMACBZ&&benzene ring ベンゼン&& |
| − | &&BMACID&&indole ring&& | + | &&BMACID&&indole ring インドール&& |
| − | &&BMACPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | + | &&BMACPL&&pyrrolidine ring ピロリジン&& |
| − | &&BMACIZ&&imidazole ring&& | + | &&BMACIZ&&imidazole ring イミダゾール&& |
| − | + | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl 脂肪酸&& | |
| − | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | + | |
&&BMFYS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMFYS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMFYB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMFYB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| − | &&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle&& | + | &&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle 単、複合環&& |
| − | &&BMMCBZ&&benzene ring&& | + | &&BMMCBZ&&benzene ring ベンゼン環&& |
&&BMMCBZ1S&&0-1 substitution&& | &&BMMCBZ1S&&0-1 substitution&& | ||
&&BMMCBZ2O&&2 substitutions (ortho)&& | &&BMMCBZ2O&&2 substitutions (ortho)&& | ||
| Line 204: | Line 256: | ||
&&BMMCBZ4S&&with 4-6 substitutions&& | &&BMMCBZ4S&&with 4-6 substitutions&& | ||
| − | &&BMMCPY&&pyrimidine | + | &&BMMCPY&&pyrimidine ring ピリミジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYCT&&cytosine&& | + | &&BMMCPYCT&&cytosine シトシン&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYTY&&thymine&& | + | &&BMMCPYTY&&thymine チミン&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYUR&&uracil&& | + | &&BMMCPYUR&&uracil ウラシル&& |
| − | &&BMMCPYXX&&others&& | + | &&BMMCPYXX&&others その他&& |
| − | &&BMMCPD&&pyridine ring&& | + | &&BMMCPD&&pyridine ring ピリジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCIZ&&imidazole ring&& | + | &&BMMCIZ&&imidazole ring イミダゾール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCTZ&&thiazole ring&& | + | &&BMMCTZ&&thiazole ring チアゾール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCQN&&quinone ring&& | + | &&BMMCQN&&quinone ring キノン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCVA&&retinol ring&& | + | &&BMMCVA&&retinol ring レチノール環&& |
| − | &&BMMCPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | + | &&BMMCPL&&pyrrolidine ring ピロリジン環&& |
| − | &&BMMCLA&&lacton&& | + | &&BMMCLA&&lacton ラクトン&& |
| − | &&BMMCAC&&aliphatic cycle&& | + | &&BMMCAC&&aliphatic cycle 脂肪族環&& |
| − | &&BMMCACCH&&cyclohexane&& | + | &&BMMCACCH&&cyclohexane シクロヘキサン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACEN&&cyclohexene&& | + | &&BMMCACEN&&cyclohexene シクロヘキセン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACDE&&cyclohexadiene&& | + | &&BMMCACDE&&cyclohexadiene シクロヘキサジエン&& |
| − | &&BMMCACXX&&others&& | + | &&BMMCACXX&&others その他&& |
| − | &&BMMCHC&&hetero cyclic&& | + | &&BMMCHC&&hetero cyclic ヘテロ環&& |
| − | &&BMMCAS&&assembled&& | + | &&BMMCAS&&assembled 複合環&& |
| − | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle&& | + | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle 共役環&& |
| − | &&BMCCPU&&purine ring&& | + | &&BMCCPU&&purine ring プリン環&& |
&&BMCCPUAD&&アデニン(アデニン、ヌクレオシド)&& | &&BMCCPUAD&&アデニン(アデニン、ヌクレオシド)&& | ||
&&BMCCPUAP&&アデニン(ヌクレオチド)&& | &&BMCCPUAP&&アデニン(ヌクレオチド)&& | ||
| Line 250: | Line 302: | ||
&&BMCCBR&&bridged structure 架橋環構造&& | &&BMCCBR&&bridged structure 架橋環構造&& | ||
| − | &&BMXX&&Others&& | + | &&BMSUM4&&monosaccharide (4 carbons) 単糖(4炭素)&& |
| + | &&BMSUM4A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM4K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM4H&&sugar alcohol 糖アルコール&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUM5&&monosaccharide (5 carbons) 単糖(5炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5H&&sugar alcohol 糖アルコール&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5N&&amino sugar アミノ糖&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5U&&uronic acid ウロン酸&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM5L&&saccharic lactone 糖ラクトン&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUM6&&monosaccharide (6 carbons) 単糖(6炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6H&&sugar alcohol 糖アルコール&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6N&&amino sugar アミノ糖&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6U&&uronic acid ウロン酸&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM6L&&saccharic lactone 糖ラクトン&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUM7&&monosaccharide (7 carbons) 単糖(7炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM7A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM7K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM7U&&uronic acid ウロン酸&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUM8&&monosaccharide (8 carbons) 単糖(8炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM8A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM8K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM8U&&uronic acid ウロン酸&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUM9&&monosaccharide (9 carbons) 単糖(9炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM9A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM9K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUM9U&&uronic acid ウロン酸&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUD2&&disaccharide (12 carbons) 二糖(12炭素)&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUD2A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUD2K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUD2H&&sugar alcohol 糖アルコール&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUD2N&&amino sugar アミノ糖&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMSUPn&&polysaccharide 多糖&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUP2A&&aldose アルドース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUP2K&&ketose ケトース&& | ||
| + | &&BMSUP2N&&amino sugar アミノ糖&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMXX&&Others その他&& | ||
&&BMXXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | &&BMXXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
&&BMXXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | &&BMXXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
---> | ---> | ||
| − | + | {{Doc:SysName}} | |
Latest revision as of 13:46, 2 June 2011
Basic Metabolism (基礎代謝)
| Basic Metabolism Top (代謝トップ) |
Molecule Index (化合物索引) |
EC classes ( EC分類) |
Input New Data (新規入力) |
Contents |
[edit] 概要
|
(The following description is translated from an article written by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.)
|
(以下の情報は共立出版バイオインフォマティクス事典で有田の執筆項目「代謝」より、出版社の許可を得て転載)
|
[edit] Metabolite Category
[edit] Design of Basic Metabolite ID numbers ID番号の設計
12-DIGIT
| B | M | a | a | b | b | c | c | d | d | e | e |
|
|
|
[edit] Systematic Name of Enzymes (酵素のシステム名)
|
EC (Enzyme Commission) number is assigned according to the type of reaction catalysed (EC level 1) and the type(s) of the substrate(s). Since reactions are written for the purpose of classification, the direction does not reflect the actually demonstrated catalysis. The systematic name always reflects the first enzyme-catalysed step, and subsequent transformations are written in parentheses, e.g. acetyl-CoA:glyoxylate C-acetyltransferase (thioester-hydrolysing, carboxymethyl-forming) (EC 2.3.3.9). |
EC番号は酵素反応のタイプおよび基質(反応物)のタイプによって分類されます。分類を目的として反応式を記すため方向は実際に観測された向きと異なる場合があります。システム名は常に酵素で触媒される最初のステップを表現しており、続く反応ステップは括弧の中に書きます。例:acetyl-CoA:glyoxylate C-acetyltransferase (thioester-hydrolysing, carboxymethyl-forming) (EC 2.3.3.9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[edit] Systematic Name of Metabolites (代謝物のシステム名)
準備中
Subcategories
This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.