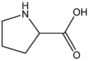Category:BM
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
&&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | &&BM&&Basic Metabolites&& | ||
&&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | &&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | ||
| + | &&BMIOOX&&oxidized elements 酸化物(no C)&& | ||
| + | &&BMIOMT&&metals and halogens 金属、ハロゲン&& | ||
| + | &&BMIONT&&nitrogen compounds 窒素&& | ||
| + | &&BMIOPP&&phosphates リン酸&& | ||
| + | &&BMIOSF&&sulfates 硫黄&& | ||
| + | |||
&&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | &&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | ||
| + | &&BMAAS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
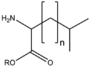
| + | &&BMAAB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| + | |||
&&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives&& | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives&& | ||
| + | &&BMAXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
| + | &&BMAXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
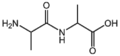
| + | &&BMAXDP&&di-peptide&& | ||
| + | &&BMAXTP&&tri-peptide&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMAC&&Cyclic amino acids&& | ||
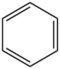
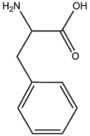
| + | &&BMACBZ&&benzene ring&& | ||
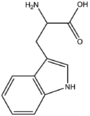
| + | &&BMACID&&indole ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMACPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | ||
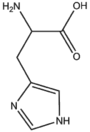
| + | &&BMACIZ&&imidazole ring&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
&&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | ||
| − | && | + | &&BMFYS&&straight chain 鎖状&& |
| + | &&BMFYB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
| + | |||
&&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle&& | &&BMMC&&mono- or assembled cycle&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ&&benzene ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ1S&&0-1 substitution&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ2O&&2 substitutions (ortho)&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ2M&&with 2 substitutions (meta)&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ2P&&with 2 substitutions (para)&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ3S&&with 3 substitutions&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCBZ4S&&with 4-6 substitutions&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMMCPY&&pyrimidine ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCPYCT&&cytosine&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCPYTY&&thymine&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCPYUR&&uracil&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCPYXX&&others&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMMCPD&&pyridine ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCIZ&&imidazole ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCTZ&&thiazole ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCQN&&quinone ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCVA&&retinol ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCPL&&pyrrolidine ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCLA&&lacton&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCAC&&aliphatic cycle&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCACCH&&cyclohexane&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCACEN&&cyclohexene&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCACDE&&cyclohexadiene&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCACXX&&others&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCHC&&hetero cyclic&& | ||
| + | &&BMMCAS&&assembled&& | ||
| + | |||
| + | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPU&&purine ring&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPUAD&&アデニン(アデニン、ヌクレオシド)&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPUAP&&アデニン(ヌクレオチド)&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPUGU&&グアニン(グアノシン)&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPUXA&&キサンチン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPT&&pteridine ring プテリジン環&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPTFL&&flavin フラビン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPTFO&&folic acid 葉酸&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPTPT&&others その他のプテリジン類&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPP&&porphyrin ring ポルフィリン環&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPPO&&pyrrole ピロール&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPPR&&porphyrinogen ポルフィリノーゲン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPHM&&heme ヘム&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPPC&&precorrin プレコリン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPCB&&cobalamin コバラミン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPCL&&chlorophyl クロロフィル&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCPPBL&&bilirubin ビリルビン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCID&&indole インドール&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCVE&&tocopherol トコフェロール(ビタミンE)&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCQI&&quinoline キノリン&& | ||
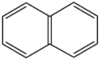
| + | &&BMCCNP&&naphthalen ナフタレン&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCCC&&condensed rings その他の縮合環&& | ||
| + | &&BMCCBR&&bridged structure 架橋環構造&& | ||
| + | |||
&&BMXX&&Others&& | &&BMXX&&Others&& | ||
| + | &&BMXXS&&straight chain 鎖状&& | ||
| + | &&BMXXB&&branched chain 分岐&& | ||
---> | ---> | ||
==Biosynthesis 生合成== | ==Biosynthesis 生合成== | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 4 September 2008
Basic Metabolites (基礎代謝物)
Class Overview
(The following description is translated from an article by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.)
Metabolism is the total body of physicochemical reactions inside living systems. It can be functionally divided into two groups: the basic (or primary) metabolism essential for maintenance of life systems, and the non-essential secondary metabolism. Basic metabolites therefore include bases, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids (building blocks of DNA, protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively). Also included are lignin and cellulose which are essential for plant growth. On the other hand, the secondary metabolism provides species-specific functions. It includes medicinal metabolites such as antibiotics and herbal medicines.
Biosynthesis 生合成
Subcategories
This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.