Category:BM
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|align="center"|[[:Category:BMIO|BMIO: Inorganics]]<br>無機物<br>[[Image:BMIO.png|100px]]<br>metals, phosphates etc.<br>金属、燐酸等 | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMIO|BMIO: Inorganics]]<br>無機物<br>[[Image:BMIO.png|100px]]<br>metals, phosphates etc.<br>金属、燐酸等 | ||
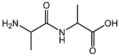
|align="center"|[[:Category:BMAA|BMAA: Amino acids]]<br>アミノ酸<br>[[Image:BMAA.png|100px]]<br>proper amino acids | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMAA|BMAA: Amino acids]]<br>アミノ酸<br>[[Image:BMAA.png|100px]]<br>proper amino acids | ||
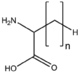
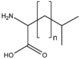
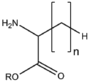
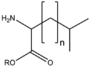
| − | |align="center"|[[:Category: | + | |align="center"|[[:Category:BMAX|BMAX: Amino acid derivatives]]<br>アミノ酸誘導体<br>[[Image:BMAX.png|120px]]<br>peptides etc.<br>修飾物、ペプチド等 |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|align="center" valign="center"| | |align="center" valign="center"| | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
! colspan="2"|2nd Class | ! colspan="2"|2nd Class | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category: | + | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXSn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Straight chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXSn.png|90px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category: | + | |[[:Category:BMAX|BMAXBn]]||[[:Category:BMAX|Branched chain]]<br>[[Image:BMAXBn.png|90px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category: | + | |[[:Category:BMAXCC|BMAXCC]]||[[:Category:BMAXCC|Cyclic]]<br>[[Image:BMAXCC.png|90px]] |
|- | |- | ||
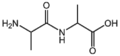
| − | |[[:Category: | + | |[[:Category:BMAXDP|BMAXDP]]||[[:Category:BMAXDP|Dipeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXDP.png|120px]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[:Category: | + | |[[:Category:BMAXTP|BMAXTP]]||[[:Category:BMAXTP|Tripeptide]]<br>[[Image:BMAXTP.png|120px]] |
|} | |} | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
&&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | &&BMIO&&Inorganics&& | ||
&&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | &&BMAA&&Amino acids&& | ||
| − | && | + | &&BMAX&&Amino acid derivatives&& |
&&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | &&BMFY&&Fatty acyl&& | ||
&&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle&& | &&BMCC&&Conjugated cycle&& | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 23 June 2008
BM: Basic Metabolites 基礎代謝物
(The following description is translated from an article by Arita in "Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics" under the publisher's permission, Kyoritsu Co. Ltd.)
Metabolism is the total body of physicochemical reactions inside living systems. It can be functionally divided into two groups: the basic (or primary) metabolism essential for maintenance of life systems, and the non-essential secondary metabolism. Basic metabolites therefore include bases, amino acids, sugars, and fatty acids (building blocks of DNA, protein, carbohydrate, and fat, respectively). Also included are lignin and cellulose which are essential for plant growth. On the other hand, the secondary metabolism provides species-specific functions. It includes medicinal metabolites such as antibiotics and herbal medicines.
Biosynthesis 生合成
Subcategories
This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.